A) rete testis.
B) ductus deferens.
C) seminal receptacle.
D) seminiferous tubule.
E) ejaculatory duct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following events in correct sequence: (1) inflation and rigidity of erectile tissue (2) arteries supplying blood to erectile tissue dilate (3) blood fills erectile tissue sinusoids and compresses veins
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 2, 3, 1
C) 3, 2, 1
D) 2, 1, 3
E) 1, 3, 2
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
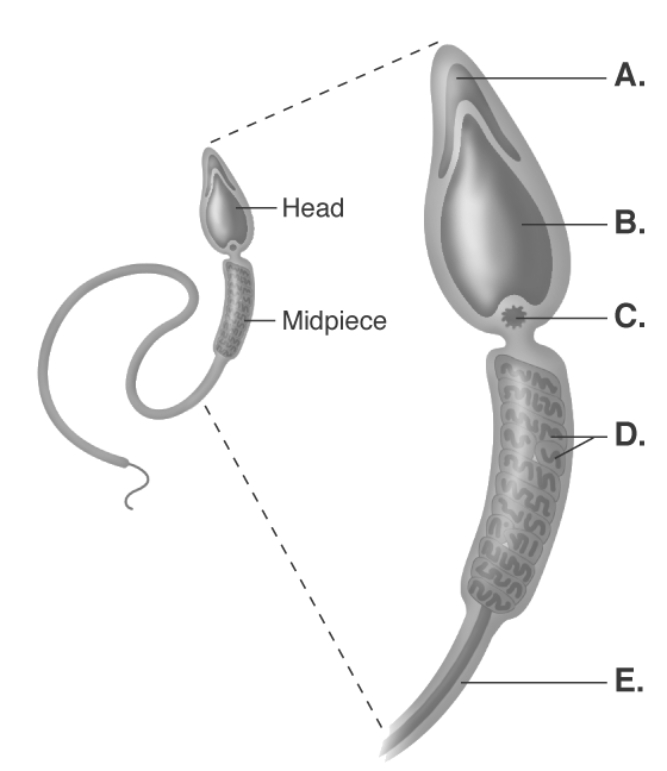 -This is a picture of a spermatozoon. What does "C" represent?
-This is a picture of a spermatozoon. What does "C" represent?
A) mitochondria
B) acrosome
C) tail
D) centriole
E) nucleus
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
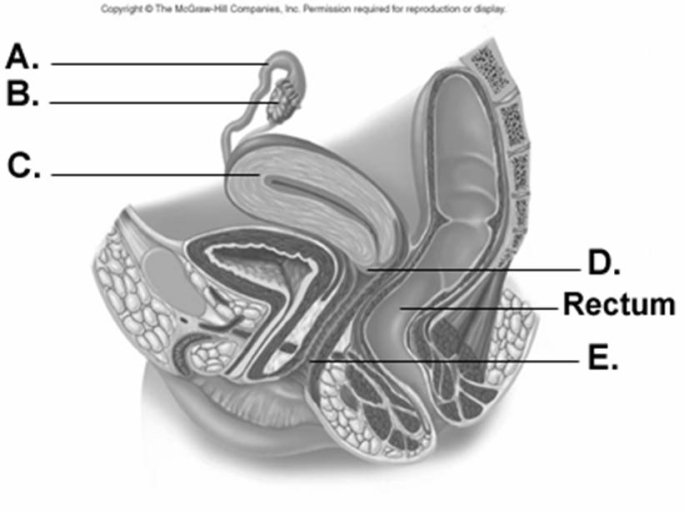 -What does "E" on the diagram represent?
-What does "E" on the diagram represent?
A) vagina
B) cervix
C) uterus
D) ovary
E) uterine tube
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The female climacteric refers to the
A) cessation of menstruation.
B) time from the onset of irregular menstrual cycles to cessation of those cycles.
C) decrease in the sexual drive.
D) inability to have sexual intercourse.
E) PMS.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the function with the correct structure. -corpus luteum
A) ovary
B) uterus
C) pituitary gland (hypophysis)
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -This is a picture of a spermatozoon. What does "A" represent?
-This is a picture of a spermatozoon. What does "A" represent?
A) mitochondria
B) acrosome
C) tail
D) centriole
E) nucleus
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following glands, choose the arrangement that represents the order in which the glands release their secretions to form semen. (1) prostate gland (2) bulbourethral glands (3) seminal vesicles
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 2, 1, 3
C) 3, 1, 2
D) 3, 2, 1
E) 2, 3, 2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
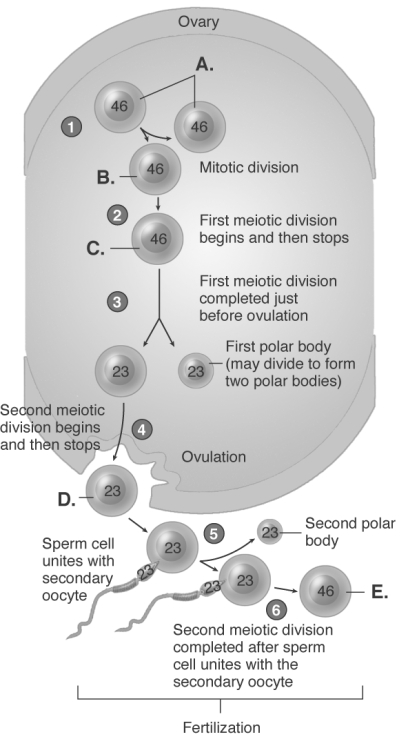 -The diagram illustrates the ovary and ovulation. What does "C" represent?
-The diagram illustrates the ovary and ovulation. What does "C" represent?
A) zygote
B) secondary oocyte
C) daughter cell
D) oogonia
E) primary oocyte
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
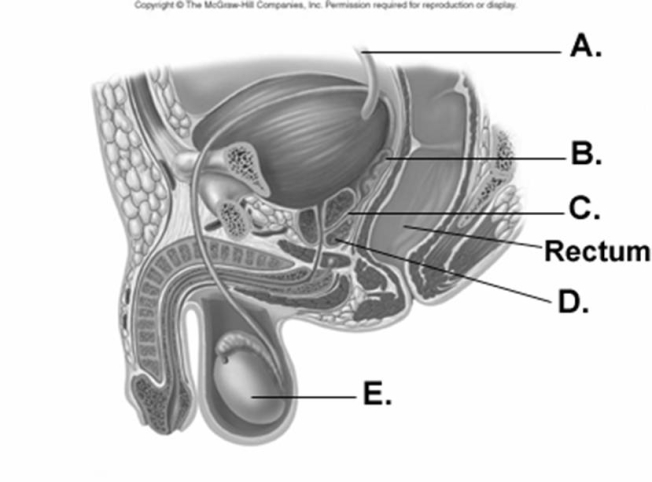 -What does "E" represent on the diagram?
-What does "E" represent on the diagram?
A) seminal vesicle
B) ejaculatory duct
C) ureter
D) testis
E) prostate gland
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Luteinizing hormone (LH) binds to interstitial (Leydig) cells and
A) inhibits sustentacular cells.
B) promotes sperm cell production by the interstitial cells.
C) decreases testosterone production by the interstitial cells.
D) stimulates GnRH levels to increase in the testes.
E) increases testosterone production by the interstitial cells.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary oocyte with a single layer of granulosa cells is most appropriately called
A) a primordial follicle.
B) a secondary follicle.
C) a mature follicle.
D) the corpus luteum.
E) a graafian follicle.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fertilization can only occur
A) if orgasms occur in both the male and female.
B) when a sperm cell penetrates a secondary oocyte.
C) when there is no menstrual flow.
D) after oxytocin is released from the hypothalamus.
E) on day 14 of the cycle.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -suspensory ligament
A) attaches the ovary to the superior margin of the uterus
B) extends from the uterus through the inguinal canal to the external genitalia
C) spreads out on both sides of the uterus; is attached to the ovaries and oviducts
D) extends from the mesovarium to the body wall
E) attaches the ovaries to the broad ligament
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hypothalamic hormone that regulates both male and female reproductive cycles is
A) FSH.
B) ICSH.
C) GnRH.
D) LH.
E) oxytocin.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following substances are found in the secretions of the prostate gland?
A) mucous and fibrinogen
B) fructose and mucous
C) fibrinolysin and clotting factors
D) prostaglandins and sperm
E) acid and mucous
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Zygote" is the term used to describe the
A) Graafian oocyte.
B) primary oocyte.
C) secondary oocyte.
D) fertilized oocyte.
E) sperm just before fertilization.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ductus deferens
A) stores sperm until ejaculation.
B) travels through the bladder.
C) ascends the abdominal cavity along the posterior side of the kidney.
D) passes through the inguinal canal and enters the pelvic cavity.
E) passes just beneath the skin to the penis.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average menstrual cycle is about ____ days long; ovulation occurs on about day ____.
A) 30; 24
B) 28; 14
C) 24; 14
D) 20; 10
E) 32; 16
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an age-related change of the female reproductive system?
A) dryness of the vagina
B) decreased estrogen and progesterone production
C) cessation of the menses
D) decreased incidence of breast cancer
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 189
Related Exams