A) mature to form sperm cells.
B) produce testosterone.
C) provide nourishment for development of sperm.
D) cover and protect most of the testes.
E) produce seminal fluid.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -round ligament
A) attaches the ovary to the superior margin of the uterus
B) extends from the uterus through the inguinal canal to the external genitalia
C) spreads out on both sides of the uterus; is attached to the ovaries and oviducts
D) extends from the mesovarium to the body wall
E) attaches the ovaries to the broad ligament
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gradual increase in estrogen secretion during the follicular phase is the result of
A) declining FSH levels.
B) granulosa cells converting androgens to estrogen.
C) positive feedback on the anterior pituitary.
D) an LH surge.
E) luteal development.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sexual drive in females
A) is dependent on hormones.
B) can be affected by psychological factors.
C) is influenced by androgens that affect the hypothalamus.
D) is dependent on hormones, can be affected by psychological factors, and is influenced by androgens that affect the hypothalamus.
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ovary is attached to the superior margin of the uterus by the
A) mesovarium.
B) broad ligament.
C) ovarian ligament.
D) suspensory ligament.
E) round ligament.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
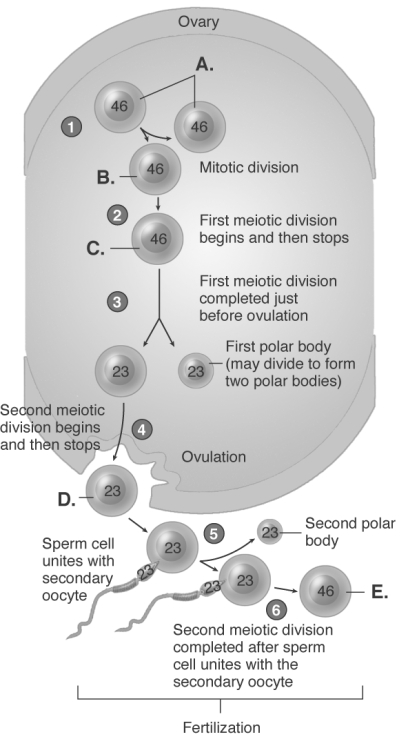 -The diagram illustrates the ovary and ovulation. What does "E" represent?
-The diagram illustrates the ovary and ovulation. What does "E" represent?
A) zygote
B) secondary oocyte
C) daughter cell
D) oogonia
E) primary oocyte
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary spermatocyte is a diploid cell that gives rise to two secondary spermatocytes after the first meiotic division. The primary spermatocyte has
A) 92 chromosomes.
B) 46 chromosomes.
C) 23 chromosomes.
D) 13 chromosomes.
E) no chromosomes.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -labia minora
A) longitudinal skin folds that border the vestibule
B) small erectile structure homologous to the penis
C) a fold formed by the anterior fusion of the labia minora
D) two hair-covered folds of skin lateral to the labia minora
E) both the vagina and urethra open into this space
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following hormones is detected by over-the-counter pregnancy kits?
A) progesterone
B) estrogen
C) prolactin
D) human chorionic gonadotropin
E) oxytocin
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the hormone with the correct function. -FSH
A) stimulates development of male sex organs
B) stimulates interstitial cells to produce testosterone
C) initiates development of primary follicles
D) causes hypertrophy of endometrium
E) stimulates synthesis of progesterone receptors
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cell types is formed at the end of the first meiotic division?
A) spermatid
B) spermatogonia
C) primary spermatocyte
D) secondary spermatocyte
E) spermatozoa
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A blood test for the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is useful in the diagnosis of
A) prostatitis.
B) prostatic atrophy.
C) prostatic cancer.
D) prostatic infection.
E) urinary tract infection.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Menstrual cramps are most commonly caused by
A) increased FSH levels.
B) increased estrogen secretion by the ovary.
C) increased prostaglandin secretions.
D) increased HCG hormone release.
E) a decreased inflammatory response in the endometrium.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The release of the secondary oocyte from the ovary is called
A) ovulation.
B) fertilization.
C) sporulation.
D) implantation.
E) oocyte release.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trace the pathway of an egg as it passes through the uterine tube. (1) ampulla (2) fimbriae (3) infundibulum (4) isthmus
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 2, 4, 1, 3
C) 3, 4, 1, 2
D) 2, 3, 1, 4
E) 3, 1, 2, 4
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The secretions produced by the prostate gland
A) are acidic.
B) contain fructose.
C) contain mucous.
D) constitute about 30% of the semen.
E) constitute about 90% of the semen.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
A) broad ligaments - help support the uterus
B) cervix - lined with rugae
C) basal layer - layer of endometrium closest to uterine cavity
D) perimetrium - muscular coat of uterus
E) endometrium - connective tissue layer
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the function with the correct structure. -ovulation
A) ovary
B) uterus
C) pituitary gland (hypophysis)
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
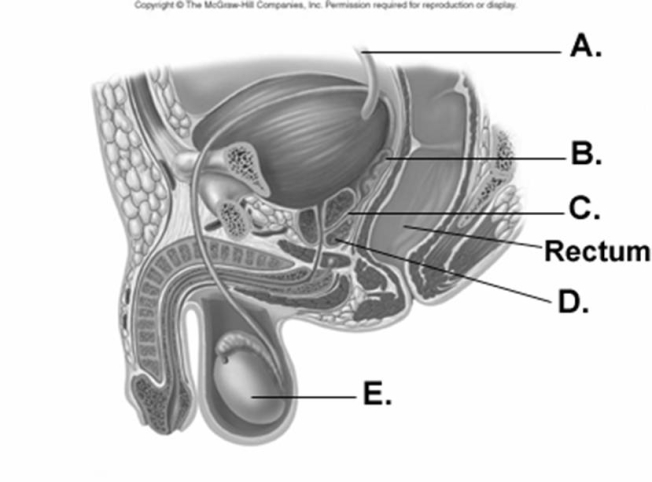 -What does "B" represent on the diagram?
-What does "B" represent on the diagram?
A) seminal vesicle
B) ejaculatory duct
C) ureter
D) testis
E) prostate gland
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is produced in the ovary and then leaves the ovary?
A) testosterone
B) corpus luteum
C) secondary oocyte
D) FSH
E) menstrual blood
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 189
Related Exams