A) the floor of the nasal cavity
B) superior portion of pharynx
C) a soft process that extends inferiorly from the posterior edge of the soft palate
D) the opening of the nasal cavity into the pharynx
E) external openings of the nasal cavity
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following laryngeal cartilages are paired? (1) epiglottis (2) thyroid cartilage (3) corniculate cartilage (4) arytenoid cartilage (5) cuneiform cartilage (6) cricoid cartilage
A) 1, 2, 6
B) 3, 5, 6
C) 2, 4, 5
D) 3, 4, 5
E) 2, 3, 4
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bohr effect refers to the
A) mechanism involved in diffusion of nitrogen into the blood.
B) physical laws governing the solubility of gases in fluids.
C) effect of pH on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
D) chemical equilibrium between carbonic acid and bicarbonate in the blood.
E) effect of temperature on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ring of cartilage that forms the base of the larynx is the
A) epiglottis.
B) thyroid cartilage.
C) cricoid cartilage.
D) arytenoid cartilage.
E) cuneiform cartilage.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following two choices. -increase in pH
A) oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts to the right
B) oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts to the left
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What factors are responsible for the decrease in the volume of the alveoli?
A) compliance and lung recoil
B) lung recoil and surface tension of water
C) compliance and surface tension of water
D) perfusion and lung recoil
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
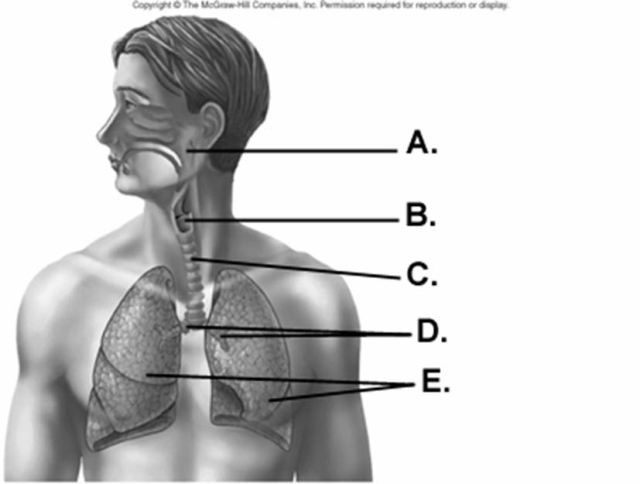 -What does "C" represent on the diagram?
-What does "C" represent on the diagram?
A) larynx
B) lungs
C) trachea
D) pharynx
E) bronchi
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mr. Huff and Puff is getting ready to blow up a pool float because he can't find the air pump. He takes a big breath in after exhaling normally. The air he takes in is the
A) inspiratory reserve volume.
B) vital capacity.
C) inspiratory capacity.
D) tidal volume.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient has severe pneumonia, which has thickened the respiratory membrane. Despite oxygen therapy, he still has rapid respiration and feels as if he is not getting enough air. This is because
A) the oxygen increases the stimulation of the carotid and aortic bodies.
B) the oxygen stimulates the respiratory center to increase the respiratory rate.
C) his blood pH increased and stimulated an increase in his respiratory rate.
D) even though he is receiving enough oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions accumulate in his blood and cause the respiratory rate to continue to increase.
E) oxygen cannot diffuse across the thickened membrane.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the appropriate description or definition. -residual volume "Enter the letter of the correct description below"
A) sum of the inspiratory reserve, expiratory reserve, tidal, and residual volumes
B) volume of air inspired during a normal inspiration
C) volume of air remaining in lungs after the most forceful expiration
D) sum of the expiratory reserve, inspiratory reserve, and tidal volumes
E) the amount of air that can be forcefully expired after expiration of the normal tidal volume
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) bronchitis - inflammation of the bronchi
B) emphysema - destruction of the alveolar walls
C) pulmonary fibrosis - loss of elastic recoil in the lung
D) cystic fibrosis - replacement of lung tissue with fibrous connective tissue
E) smokers - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than is oxygen. Which gas has the higher rate of diffusion?
A) carbon dioxide
B) oxygen
C) Both will have the same rate of diffusion
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the appropriate description or definition. -expiratory reserve volume "Enter the letter of the correct description below"
A) sum of the inspiratory reserve, expiratory reserve, tidal, and residual volumes
B) volume of air inspired during a normal inspiration
C) volume of air remaining in lungs after the most forceful expiration
D) sum of the expiratory reserve, inspiratory reserve, and tidal volumes
E) the amount of air that can be forcefully expired after expiration of the normal tidal volume
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A baby holding its breath will
A) be termed a "blue baby".
B) have brain cells damaged because of low blood oxygen levels.
C) suffer heart damage because of increased pressure in the aorta.
D) automatically start to breathe when the CO2 levels in the blood reach a high enough value.
E) automatically start to breathe when oxygen levels decrease slightly.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Hering-Breuer reflex
A) causes erratic respirations.
B) helps prevent overinflation of the lungs.
C) has its sensory components in the sympathetic nerves.
D) is a normal response to increased oxygen content in the blood.
E) limits how much air a person can expire.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged across the respiratory membrane by the process of
A) active transport.
B) diffusion.
C) filtration.
D) osmosis.
E) cotransport.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a respiratory adaptation to exercise training?
A) vital capacity increases
B) tidal volume at maximal exercise will increase
C) increased minute ventilation after training
D) after training, respiratory rate at rest is lower
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following two choices. -increase in body temperature
A) oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts to the right
B) oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts to the left
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following structures, the largest in diameter is the
A) primary bronchus.
B) secondary bronchus.
C) respiratory bronchiole.
D) trachea.
E) tertiary bronchus.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Contraction of the _______ will increase the superior-inferior dimension of the thoracic cavity.
A) rectus abdominis
B) internal intercostals
C) diaphragm
D) external intercostals
E) sternocleidomastoid
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 178
Related Exams