Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hemoglobin
A) gives white blood cells their color.
B) transports oxygen in the blood.
C) is normally found in both the plasma and erythrocytes.
D) catalyzes the reaction that forms carbonic acid.
E) is only used once then decomposed.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When large quantities of blood are lost, erythrocytes must be replaced to restore
A) the body's ability to fight infection.
B) oxygen-carrying capacity.
C) thrombin levels.
D) normal blood pH.
E) iron levels.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Agglutination of red blood cells means
A) they rupture.
B) they form a clot.
C) they clump together.
D) they lose their nucleus.
E) they bump into each other.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lymphocytes
A) are the largest of the leukocytes.
B) migrate to lymphatic tissue.
C) produce histamine.
D) release heparin.
E) are phagocytic.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the substance necessary for clotting with its particular role. -tissue factor
A) a mixture of lipoproteins released from injured tissue
B) converts prothrombin to thrombin
C) the insoluble protein that forms the network of the clot
D) needed by the liver to produce prothrombin
E) fibrin-stabilizing factor
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During platelet plug formation,
A) platelets stick to the exposed collagen fibers of injured vessels.
B) activated platelets release fibrinogen.
C) thrombin is released from endothelial cells.
D) vitamin K production increases.
E) platelets multiply.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a stage of hemostasis?
A) coagulation
B) erythropoiesis
C) platelet formation
D) vascular dilation
E) agglutination
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
RhoGam injections are given to
A) desensitize the fetus.
B) activate fetal Rh antigens.
C) protect the father.
D) prevent sensitization of the mother.
E) change the mother's blood type.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true of plasma?
A) Plasma is about 91% water.
B) Plasma is a colloid.
C) Plasma volume can change drastically.
D) The color of plasma is yellow.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
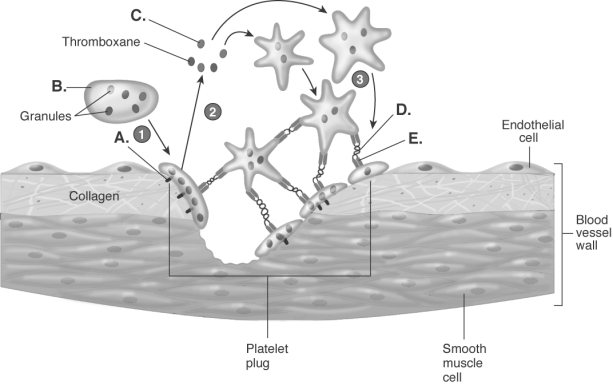 -The diagram illustrates platelet plug formation. What does "B" represent?
-The diagram illustrates platelet plug formation. What does "B" represent?
A) fibrinogen receptor
B) fibrinogen
C) platelet
D) ADP
E) von Willebrand factor
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which blood component is NOT correctly matched with its function?
A) erythrocytes - transport oxygen
B) leukocytes - protect against disease
C) platelets - phagocytize bacteria
D) plasma proteins - maintain blood osmotic pressure; involved in clotting
E) monocytes - become macrophages
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combination of hemoglobin and carbon dioxide is
A) carboxyhemoglobin.
B) oxyhemoglobin.
C) deoxyhemoglobin.
D) carbaminohemoglobin.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The plasma component that forms fibrin, the insoluble protein, in a blood clot is
A) sodium.
B) albumin.
C) globulin.
D) fibrinogen.
E) fibrinolysis.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
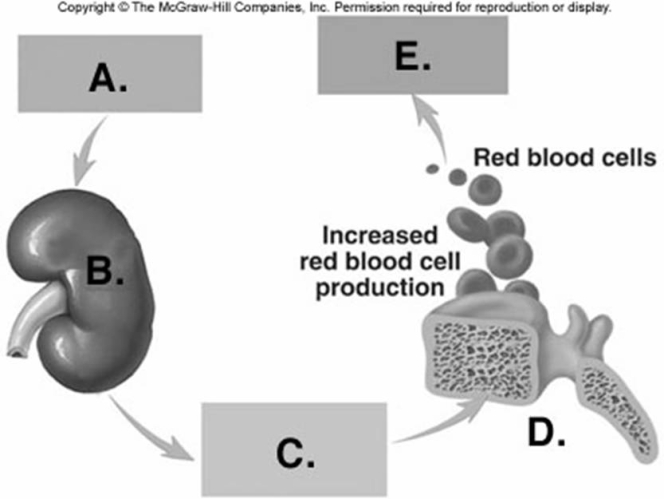 -On the diagram of RBC production, what does "A" represent?
-On the diagram of RBC production, what does "A" represent?
A) increased blood oxygen
B) decreased blood oxygen
C) erythropoietin
D) kidney
E) red bone marrow
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increased amount of heparin in the blood might
A) speed up the clotting process.
B) slow down the clotting process.
C) stop the clotting process.
D) enhance the clotting process.
E) have no effect on the clotting process.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the substance necessary for clotting with its particular role. -factor XIII
A) a mixture of lipoproteins released from injured tissue
B) converts prothrombin to thrombin
C) the insoluble protein that forms the network of the clot
D) needed by the liver to produce prothrombin
E) fibrin-stabilizing factor
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aspirin inhibits platelet plug formation by
A) blocking the binding of platelets to collagen.
B) interfering with the synthesis of prostaglandins.
C) blocking the effects of serotonin.
D) making the platelet surface less sticky.
E) stimulating the release of heparin.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the substance necessary for clotting with its particular role. -vitamin K
A) a mixture of lipoproteins released from injured tissue
B) converts prothrombin to thrombin
C) the insoluble protein that forms the network of the clot
D) needed by the liver to produce prothrombin
E) fibrin-stabilizing factor
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person with an increased eosinophil count might be suffering from
A) a parasitic worm infection.
B) a viral infection.
C) an acute bacterial infection.
D) a chronic bacterial infection.
E) a head cold.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 145
Related Exams