A) insula.
B) parietal lobe.
C) frontal lobe.
D) temporal lobe.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -CREB C
A) the part of the brain involved in the actual declarative memory
B) the largest of the cerebral commissures
C) a factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) a series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) a part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning the descending pathways of the spinal cord is true?
A) Most descending pathways control sensory functions.
B) Many of the descending pathways decussate in the midbrain.
C) Descending pathways consist of upper and lower motor neurons.
D) Descending pathways must synapse in the thalamus.
E) These pathways start in the spinal cord and end in the brain.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During brain surgery, the superior portion of the primary somatic sensory cortex of a patient is stimulated. The patient is most likely to
A) flex his fingers.
B) talk to the surgeon.
C) smile.
D) feel something touching his back.
E) wiggle his toes.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary function of the cerebellum is to
A) interpret sound.
B) coordinate movement.
C) control body temperature.
D) regulate consciousness.
E) regulate sleep patterns.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
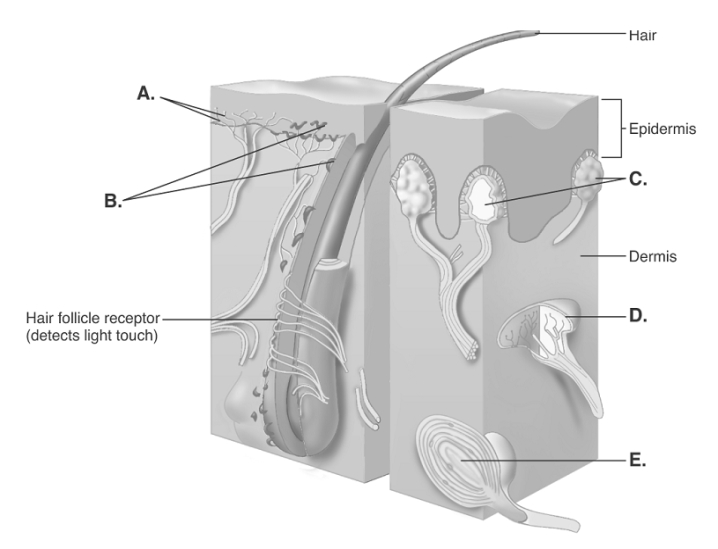 HAPS Objective: H06.01 Describe exteroceptors, interoceptors and proprioceptors in terms of the general location of each in the body and the origin of the stimuli that each receives.
HAPS Objective: H06.02 Describe each of the following types of receptors, indicating what sensation it detects and giving an example of where it can be found in the body- pain receptors (nociceptors) , temperature receptors, mechanoreceptors (including proprioceptors and barorceptors/pressoreceptors) , chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors.
HAPS Objective: H06.03 Explain the generator potential that occurs when receptors for general senses are stimulated.
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "E"?
HAPS Objective: H06.01 Describe exteroceptors, interoceptors and proprioceptors in terms of the general location of each in the body and the origin of the stimuli that each receives.
HAPS Objective: H06.02 Describe each of the following types of receptors, indicating what sensation it detects and giving an example of where it can be found in the body- pain receptors (nociceptors) , temperature receptors, mechanoreceptors (including proprioceptors and barorceptors/pressoreceptors) , chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors.
HAPS Objective: H06.03 Explain the generator potential that occurs when receptors for general senses are stimulated.
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "E"?
A) detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) responds to painful stimuli
C) responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) detects continuous touch or pressure
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The simplest and most common type of sensory nerve endings are free nerve endings.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a somatic sense?
A) smell
B) taste
C) touch
D) sound
E) sight
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
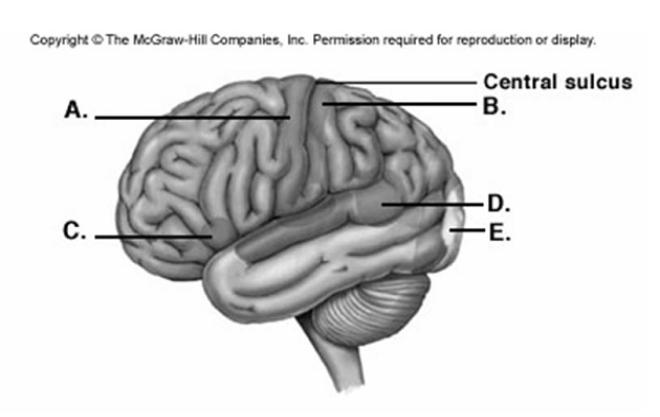 -Label area "E" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "E" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca'sarea)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary motor area
A) contains sensory neurons for the face in its inferior portion.
B) contains a smaller area for control of the hands than for control of the legs.
C) contains neurons that control smooth muscle.
D) contains more motor neurons for the thighs than the mouth.
E) contains a larger area for control of the hand and fingers than for control of the arm and elbow.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to the cerebellum is likely to cause
A) decreased muscle tone.
B) balance impairment.
C) the tendency to overshoot when reaching for an object.
D) an intention tremor.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the sensation with the appropriate receptor type. -Ruffini end organs A
A) mechanoreceptors
B) thermoreceptors
C) nociceptors
D) chemoreceptors
E) photoreceptors
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Label area "A" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "A" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cerebellum?
A) learning to play the harp.
B) keeping time with music
C) sleep-wake cycle
D) coordination of skeletal muscles
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The extrapyramidal system
A) controls the speed of skilled movements.
B) maintains control of unconscious movements.
C) interprets cutaneous perception.
D) projects sensory information from the medulla to the cerebrum.
E) control facial expression, mastication, and tongue movements.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus would help us
A) perceive pain.
B) tell if an object is rough or smooth.
C) sense temperature.
D) move our arms and legs.
E) write a sentence.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
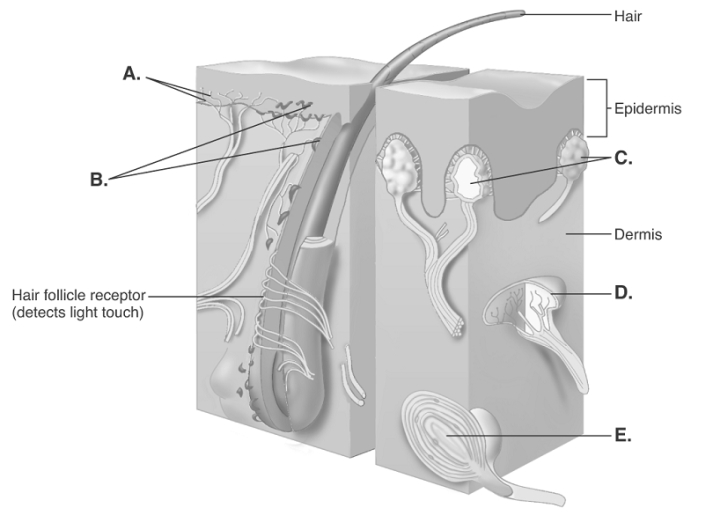 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "C" represent?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "C" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The size of various regions of the primary somatic sensory cortex is proportional to the _______ sensory receptors in that area of the body.
A) size of
B) location of
C) number of
D) size of muscles in
E) position of the
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptors that in general do not produce an action potential, but can release neurotransmitters in response to a receptor potential are
A) phasic receptors.
B) primary receptors.
C) secondary receptors.
D) tonic receptors.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lesions on one side of the spinal cord cut the lateral spinothalamic tract and eliminate
A) sensations of touch from both sides below the level of injury.
B) proprioception on the same side of the body below the level of the injury.
C) cutaneous sensations on the opposite side of the body below the level of injury.
D) sensations of vibration on the opposite side of the body at the level of the injury.
E) sensations of tickle on the same side of the body below the level of injury.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 132
Related Exams