A) rubrospinal and corticospinal.
B) spinothalamic and tectospinal.
C) vestibulospinal and rubrospinal.
D) corticobulbar and vestibulospinal.
E) corticospinal and corticobulbar.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The sense of taste is an example of a general sense.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
All aspects of a memory are stored together in the brain.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these activities is associated with the left cerebral hemisphere in most people?
A) motor control of left side of the body
B) mathematics and speech
C) spatial perception
D) recognition of faces
E) musical ability
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient has suffered a cerebral hemorrhage that has damaged the primary motor area of his right cerebral cortex. As a result the
A) patient cannot voluntarily move his right arm or leg.
B) patient feels no sensations on the left side of his body.
C) patient cannot voluntarily move his left eye.
D) patient's heart stops beating.
E) patient cannot voluntarily move his left arm or leg.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a descending pathway in the spinal cord?
A) fasciculus gracilis
B) corticospinal tract
C) spinothalamic tract
D) spinoreticular tract
E) trigeminothalamic tract
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -amygdala E
A) the part of the brain involved in the actual declarative memory
B) the largest of the cerebral commissures
C) a factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) a series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) a part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
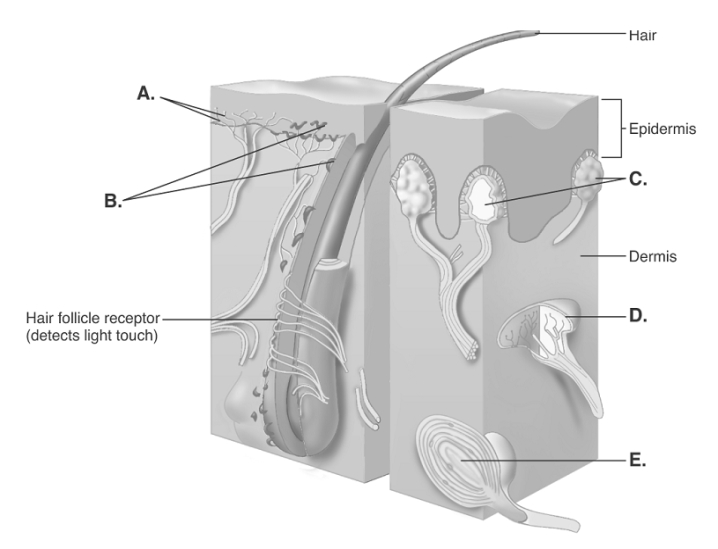 HAPS Objective: H06.01 Describe exteroceptors, interoceptors and proprioceptors in terms of the general location of each in the body and the origin of the stimuli that each receives.
HAPS Objective: H06.02 Describe each of the following types of receptors, indicating what sensation it detects and giving an example of where it can be found in the body- pain receptors (nociceptors) , temperature receptors, mechanoreceptors (including proprioceptors and barorceptors/pressoreceptors) , chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors.
HAPS Objective: H06.03 Explain the generator potential that occurs when receptors for general senses are stimulated.
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "B"?
HAPS Objective: H06.01 Describe exteroceptors, interoceptors and proprioceptors in terms of the general location of each in the body and the origin of the stimuli that each receives.
HAPS Objective: H06.02 Describe each of the following types of receptors, indicating what sensation it detects and giving an example of where it can be found in the body- pain receptors (nociceptors) , temperature receptors, mechanoreceptors (including proprioceptors and barorceptors/pressoreceptors) , chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors.
HAPS Objective: H06.03 Explain the generator potential that occurs when receptors for general senses are stimulated.
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "B"?
A) detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) responds to painful stimuli
C) responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) detects continuous touch or pressure
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an ascending pathway, axons of the secondary neuron travel from the
A) receptor to the spinal cord.
B) receptor to the brain.
C) spinal cord through the brainstem to the thalamus.
D) thalamus to the cerebral cortex.
E) spinal cord to cerebellum.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the kind of pain to the appropriate description. -chronic pain B
A) may occur in amputees
B) migraine headaches are an example of this
C) pain from internal organs sensed in the skin
D) peripheral tissue damage causes increased sensitivity in area of damage
E) increased sensitivity of CNS to tissue damage
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A series of neurons involved in long-term retention of a thought is called
A) an EEG.
B) a brain wave.
C) a memory engram.
D) short-term memory.
E) a memory trace.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) spinotectal tract - visual reflexes
B) fasciculus cuneatus - vibration from upper body half
C) spinoreticular tract - light touch
D) spinocerebellar tract - proprioception
E) spinocerebellar tract - comparator function
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Upper motor neurons
A) are found in the visual cortex.
B) control skeletal muscles.
C) are responsible for planning voluntary movements.
D) are located in the prefrontal area.
E) control smooth muscle.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vision is dependent upon
A) chemoreceptors.
B) photoreceptors.
C) thermoreceptors.
D) mechanoreceptors.
E) nociceptors.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you feel someone touch you on the shoulder, the person has stimulated a(n) ____ sense.
A) special
B) somatic
C) visceral
D) undifferentiated
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mechanoreceptors respond to
A) compression of receptors.
B) irritation of nerve endings.
C) light striking the receptors.
D) binding of molecules to membrane receptors.
E) a change in temperature.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Visceroreceptors are receptors associated with joints, tendons, and other connective tissue.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the sensation with the appropriate receptor type. -Merkel disks E
A) mechanoreceptors
B) thermoreceptors
C) nociceptors
D) chemoreceptors
E) photoreceptors
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which neurotransmitter substance has been implicated in Parkinson's disease?
A) norepinephrine
B) dopamine
C) serotonin
D) GABA
E) acetylcholine
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lesion of the basal nuclei could cause
A) loss of memory.
B) uncontrolled rage.
C) fluent but circular speech.
D) a slight shaking of the hands or head.
E) loss of sensation.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 132
Related Exams