A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Slowly adapting proprioceptors that would let you know the position of your thumb without looking at it are known as
A) phasic receptors.
B) primary receptors.
C) secondary receptors.
D) tonic receptors.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the sensation with the appropriate receptor type. -Meissner corpuscles B
A) mechanoreceptors
B) thermoreceptors
C) nociceptors
D) chemoreceptors
E) photoreceptors
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The brainstem
A) includes nuclei of cranial nerves II - XII.
B) contains centers for several vital reflexes like heart rate and blood pressure.
C) contains the reticular formation.
D) contains nuclei for vomiting and sneezing reflexes.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following result when the spinal cord is hemitransected (cut) on the left side? (1) loss of pain and thermal sensations below the injury on the left side (2) loss of pain and thermal sensations below the injury on the right side (3) loss of fine touch and pressure sensations below the injury on the left side (4) loss of fine touch and pressure sensations below the injury on right side (5) loss of fine motor control on the right side below the injury (6) loss of fine motor control on the left side below the injury
A) 1, 3, 5
B) 2, 4, 6
C) 2, 3, 6
D) 1, 3, 4, 6
E) 1, 4, 5, 6
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lesions of the limbic system might result in
A) a voracious appetite.
B) enhanced fear and anger responses.
C) decreased sexual activity.
D) loss of coordination.
E) loss of sensation.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wernicke area is necessary for
A) motivation.
B) understanding and formulating coherent speech.
C) initiating the muscular movements of speech.
D) processing visual images.
E) smiling.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nurse is caring for a patient who exhibits the following symptoms: (1) inability to maintain balance while walking (2) normal intelligence (3) can initiate voluntary movements although they are somewhat uncoordinated. (4) decreased tone in the skeletal muscles The patient is probably suffering from a condition that affected the
A) midbrain.
B) cerebellum.
C) basal ganglia.
D) cerebral cortex.
E) brainstem.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A state of conscious awareness of stimuli received by sensory receptors is called
A) adaptation.
B) projection.
C) translation.
D) perception.
E) inclination.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these activities is associated with the right cerebral hemisphere in most people?
A) adding numbers
B) reciting the Gettysburg address
C) painting a watercolor landscape
D) using a calculator
E) making a household budget
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
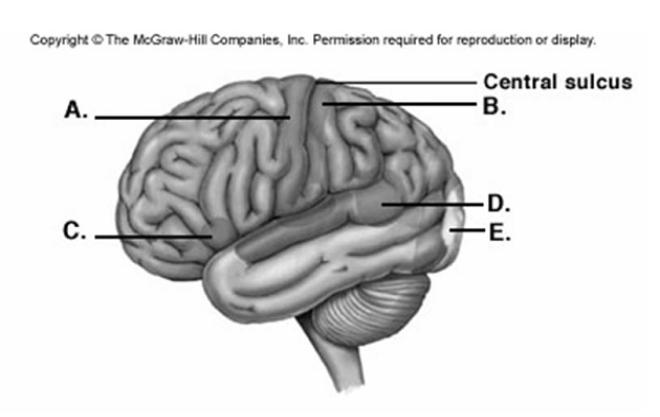 -Label area "C" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "C" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cerebellum functions as a comparator. This means that the cerebellum compares
A) the incoming sensory stimuli with the outgoing sensory stimuli.
B) intended movements with actual movements.
C) spinal cord activity with the activity of the cerebrum.
D) the right cerebellar hemisphere with the left cerebellar hemisphere.
E) and coordinates rapid, complex movements like figure skating.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ability to localize the position of body parts is called
A) two-point discrimination.
B) proprioception.
C) fine touch.
D) light touch.
E) perception.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a person decided to jump over a chair, which of the following areas organizes the motor functions needed to carry out this action.
A) visual cortex
B) premotor area
C) prefrontal area
D) auditory association area
E) visual association area
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of brain waves observed in an individual who is awake but in a quiet resting state with eyes closed are _____ waves.
A) alpha
B) beta
C) delta
D) theta
E) gamma
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long-term memory may involve
A) an influx of potassium ions into the neuron.
B) activating substance P.
C) a change in the shape of the neuron's cytoskeleton.
D) forming a nerve plexus.
E) rearranging neurons in the brain.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Procedural memory is stored primarily in the
A) hippocampus and amygdala.
B) central sulcus and Wernicke's area.
C) cerebellum and premotor area of cerebral cortex.
D) temporal lobe and frontal lobe.
E) pons and midbrain.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Broca area is damaged, the result is
A) loss of memory.
B) impairment in the movement of the right leg.
C) blindness.
D) hesitant and distorted speech.
E) inability to think of things to say.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Decreased sensitivity to a continued stimulus is called
A) adaptation.
B) projection.
C) translation.
D) conduction.
E) phantom pain.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the CNS responds to tissue damage by decreasing the pain threshold and increasing its sensitivity to pain, this is called
A) referred pain.
B) central sensitization.
C) peripheral sensitization.
D) cumulative sensitization.
E) phantom pain.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 132
Related Exams