A) concentration of potassium
B) concentration of sodium and chloride
C) negatively charged proteins
D) sodium/potassium pump
E) plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
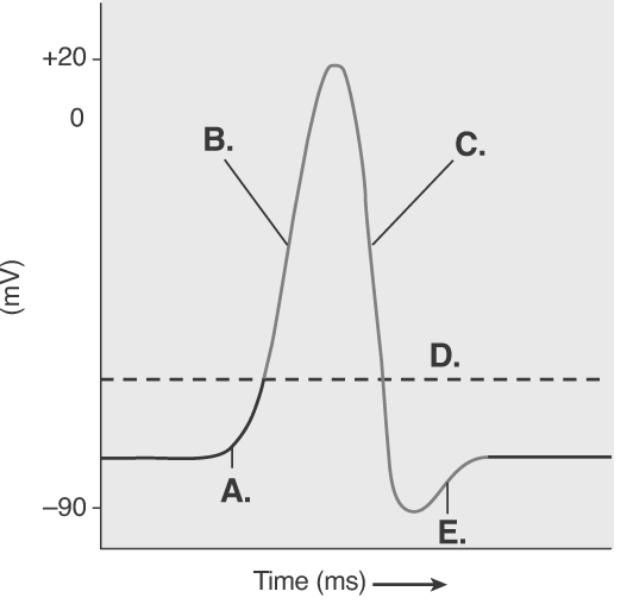 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential. What does "D" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential. What does "D" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurons arranged in a circular pathway form
A) neuromotor junctions.
B) temporal circuits.
C) reverberating circuits.
D) spatial pathways.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What ion is necessary for the release of neurotransmitter from synaptic vesicles?
A) chloride
B) sodium
C) potassium
D) calcium
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If five action potentials arrive at the same synapse in very close succession, which of the following would occur?
A) The direction of the action potential is reversed.
B) Temporal summation occurs.
C) Spatial summation occurs.
D) Hyperpolarization occurs.
E) Depolarization always occurs.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following situations occurs in electrically excitable cells?
A) When Na+ ion channels open, K+ ion channels close.
B) The sodium-potassium exchange pump moves sodium into the cell.
C) Depolarization causes voltage-gated sodium ion channels to open.
D) Ligand-gated sodium ion channels are opened by high extracellular calcium levels.
E) Proteins tend to diffuse out of the cell.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following concerning concentration differences across the plasma membrane. -postassium ions
A) concentration of potassium
B) concentration of sodium and chloride
C) negatively charged proteins
D) sodium/potassium pump
E) plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) sodium ions diffuse into the cell and cause a local potential (2) neurotransmitter binds with receptor on postsynaptic cell (3) neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) membrane permeability to sodium ions on postsynaptic cell increases (5) action potential causes release of neurotransmitter
A) 5, 2, 3, 4, 1
B) 5, 2, 3, 1, 4
C) 5, 3, 4, 1, 2
D) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
E) 5, 3, 2, 4, 1
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The strength of a stimulus is communicated through
A) changes in the magnitude of the action potential.
B) the frequency of the action potentials.
C) the length of time action potentials are produced.
D) both the frequency and the length of time action potentials are produced.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential. What does "C" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential. What does "C" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A local potential
A) does not occur until threshold.
B) transmits information from one cell to another.
C) might be a depolarization event but cannot be a hyperpolarization event.
D) increases or decreases in direct proportion to the stimulus strength.
E) does not alter resting membrane potential.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in the resting membrane potential has the following characteristics (non-propagated, graded, can summate) . This type of change can
A) be a local potential.
B) be an action potential.
C) be a consequence of an increase in the permeability to Na+.
D) result in repolarization.
E) be a local potential and a consequence of an increase in the permeability to Na+.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following situations will lead to hyperpolarization?
A) increase the permeability of the plasma membrane to Na+ ions
B) decrease the permeability of the plasma membrane to K+ ions
C) decrease the permeability of the plasma membrane to chloride ions
D) any positive ion entering the cell
E) None of these situations will lead to hyperpolarization.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO inhibitors)
A) prevent synaptic transmission.
B) enhance the breakdown of norepinephrine.
C) enhance the binding of norepinephrine to its receptors.
D) prevent the release of norepinephrine by the presynaptic terminal.
E) have no effect on the action of norepinephrine.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Action potentials at a chemical synapse
A) travel from presynaptic terminal to postsynaptic membrane.
B) travel from postsynaptic membrane to presynaptic terminal.
C) travel back and forth from presynaptic terminal to postsynaptic membrane.
D) travel from presynaptic terminal to presynaptic membrane.
E) stop at the presynaptic terminal and are regenerated on the postsynaptic membrane.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
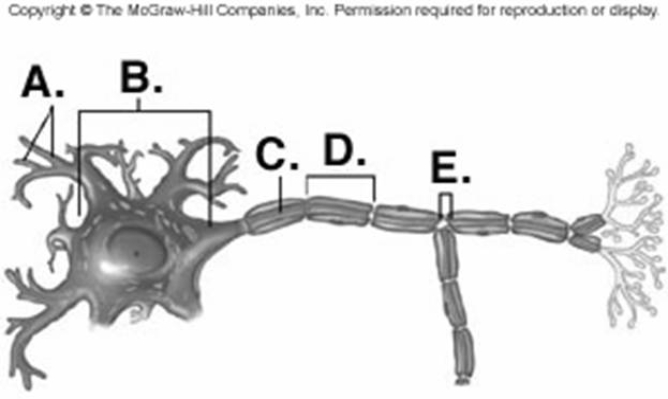 -Identify structure "E" on the neuron.
-Identify structure "E" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) neuron cell body (soma)
D) dendrites
E) axon
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential) , there is a
A) net movement of sodium ions out of the cells.
B) net movement of chloride ions into the cells.
C) decrease in action potential amplitude.
D) local hyperpolarization.
E) local depolarization.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The speed of an action potential depends upon
A) whether an axon is myelinated or not myelinated.
B) thickness of the myelin sheath.
C) the diameter of the axon.
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Identify structure "A" on the neuron.
-Identify structure "A" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) neuron cell body (soma)
D) dendrites
E) axon
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential. What does "E" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential. What does "E" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 155
Related Exams