A) ATP-binding site
B) globular (G) actin
C) calcium
D) myosin
E) sarcolemma
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the power stroke?
A) a protein found along the groove of the F-actin double helix
B) a T tubule and two adjacent terminal cisternae
C) the combination of myosin heads with active sites on actin molecules
D) the movement of myosin head while attached to actin myofilament
E) after exercise, the oxygen taken in that exceeds the oxygen required for resting metabolism
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are caveolae?
A) can rapidly develop action potentials
B) shallow invaginations of cell membrane
C) relatively constant tension maintained for a period of time
D) intracellular cytoskeleton
E) enzyme that removes phosphate from myosin
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which type of respiration does lactic acid build up in muscle fibers?
A) anaerobic respiration
B) aerobic respiration
C) both anaerobic and aerobic respiration
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Multiple wave summation
A) is a time during which the tissue cannot respond again.
B) results in complete and incomplete tetanus.
C) is a condition in which the muscle fiber only partially relaxes between contractions.
D) is a condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations.
E) is a constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smooth muscle is regulated by all of the following except
A) the autonomic nervous system.
B) neurotransmitters.
C) the somatic nervous system.
D) hormones.
E) prostaglandins.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of respiration produces ATP molecules?
A) anaerobic respiration
B) aerobic respiration
C) both anaerobic and aerobic respiration
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a function of skeletal muscle?
A) body movement
B) maintenance of posture
C) respiration
D) constriction of organs
E) production of heat
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aerobic exercise
A) increases vascularity of muscle.
B) develops fatigue-resistant fast-twitch fibers.
C) can increase the efficiency of slow-twitch fibers.
D) can increase the number of mitochondria in muscle cells.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The active sites to which cross-bridges attach are found on the
A) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) actin myofilaments.
C) Z disks.
D) T tubules.
E) myosin myofilaments.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning fast-twitch muscle fibers is true?
A) They split ATP rapidly.
B) They have large deposits of myoglobin.
C) They are well adapted to aerobic metabolism.
D) They have a well-developed blood supply.
E) They have many mitochondria.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete tetanus
A) is the time during which the tissue cannot respond again.
B) results in complete and incomplete tetanus.
C) is the condition in which the muscle fiber only partially relaxes between contractions.
D) is the condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations.
E) is the constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tetanus of a muscle is thought to be caused by
A) high calcium ion concentrations in the sarcoplasm.
B) the rapid movement of sodium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) an increase in stimulus strength.
D) increased temperature in the active muscle.
E) decreased amounts of calcium ions in muscle tissue.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the myosin head flexes into a bend, pulling the actin filament along with it, this is called the
A) action reaction.
B) power stroke.
C) recovery stroke.
D) muscle tone.
E) action potential.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange these structures as they participate in excitation-contraction.
A) T tubules, sarcolemma, calcium ions, sarcoplasmic reticulum
B) calcium ions, T tubules, sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum
C) sarcolemma, T tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium ions
D) sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium ions, T tubules, sarcolemma
E) sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium ions, T tubules
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The condition of painful, spasmodic contractions of muscles is referred to as
A) cramps.
B) fibrositis.
C) fibromyalgia.
D) muscular dystrophy.
E) paralysis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
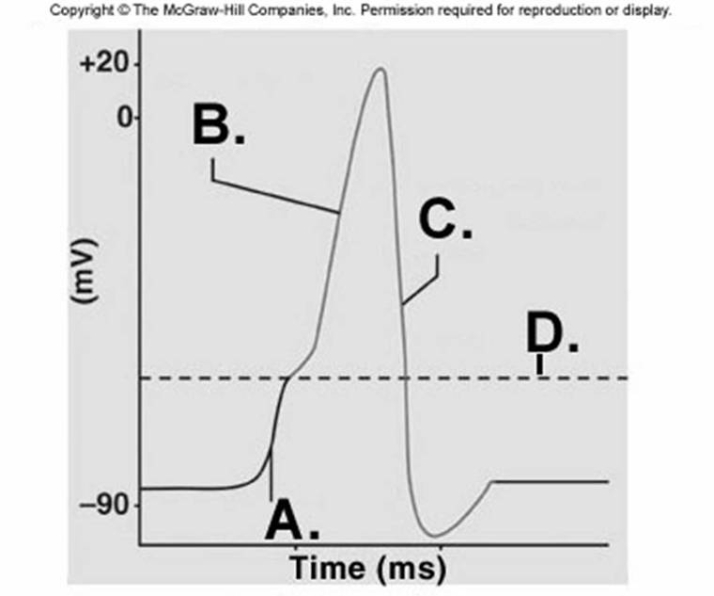 -What does "A" represent on the diagram?
-What does "A" represent on the diagram?
A) threshold
B) depolarization
C) depolarization phase of action potential
D) repolarization phase of action potential
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Multiunit smooth muscle is located in the
A) gastrocnemius.
B) wall of the GI tract.
C) wall of blood vessels.
D) wall of the heart.
E) reproductive system.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The model that describes the contraction of the muscle is called the
A) contraction cycle.
B) power stroke.
C) sliding filament model.
D) slipping fibril mechanism.
E) paddle model.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An isometric contraction is described as
A) action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
B) a muscle produces constant tension during contraction.
C) a muscle produces an increasing tension as the length remains constant.
D) a muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
E) a muscle produces tension, but the length of the muscle is increasing.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 194
Related Exams