A) increase muscle size and strength.
B) cause testicular atrophy.
C) cause cardiovascular disease.
D) increase the number of muscle fibers.
E) increase total muscle mass.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intense exercise that results in a great deal of anaerobic activity
A) converts some slow-twitch fibers into fast-twitch fibers.
B) increases muscular strength and mass.
C) enlarges slow-twitch fibers.
D) decreases the efficiency of fast-twitch fibers.
E) decreases muscle strength and mass.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Endomysium is a delicate network of loose connective tissue that
A) surrounds each muscle fiber.
B) forms a sheath around a fasciculus.
C) is composed of elastic fibers.
D) separates individual muscles.
E) penetrates muscle fibers.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The refractory period
A) is the time during which the tissue cannot respond again.
B) results in complete and incomplete tetanus.
C) is the condition in which the muscle fiber only partially relaxes between contractions.
D) is the condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations.
E) is the constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true during the resting membrane potential?
A) Sodium ion concentration is greater inside cells.
B) Negatively charged proteins are more concentrated outside the cell.
C) A greater concentration of calcium ions is found inside the cell.
D) Potassium is concentrated primarily inside the cell.
E) None of these choices reflect what occurs during the resting membrane potential.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
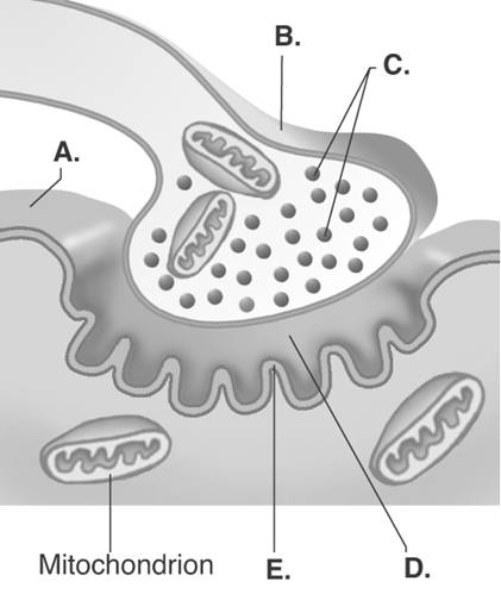 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "E" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "E" represent?
A) synaptic vesicles
B) synaptic cleft
C) sarcolemma
D) presynaptic terminal
E) postsynaptic membrane
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A child ingested an organophosphate poison used to kill insects. Soon the child's muscles began spastic contractions. Predict what occurred at the synaptic cleft.
A) decreased release of acetylcholine from presynaptic neurons
B) increased accumulation of acetylcholine in the synapse
C) the poison binds to acetylcholine receptors and stimulates them
D) increased breakdown of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
E) Both increased accumulation of acetylcholine in the synapse and increased breakdown of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the resting membrane potential becomes more negative, which of the following has occurred?
A) hyperpolarization
B) repolarization
C) depolarization
D) isopolarization
E) hypopolarization
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue has cells that branch?
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
D) both skeletal and cardiac muscle
E) both cardiac and smooth muscle
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a known effect of illegal use of anabolic steroids in large dosages?
A) increased muscle size
B) kidney damage
C) diminished testosterone secretion
D) increased cardiovascular fitness
E) sterility
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the role of pacemaker cells?
A) can rapidly develop action potentials
B) shallow invaginations of cell membrane
C) relatively constant tension maintained for a period of time
D) intracellular cytoskeleton
E) enzyme that removes phosphate from myosin
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
T tubules are invaginations of the
A) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) sarcomere.
C) myofibril.
D) sarcoplasm.
E) sarcolemma.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true of muscular atrophy?
A) It is irreversible.
B) It can be caused by disuse.
C) It can be caused by denervation.
D) Transcutaneous stimulation can help prevent it.
E) Muscle fibers are replaced by connective tissue.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding the sliding filament model is false?
A) Actin and myosin do not shorten during contraction.
B) Both actin and myosin myofilaments shorten during contraction.
C) The sarcomere shortens.
D) The I band and H zones become narrower during contraction.
E) The A band remains constant in length.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The type of neurotransmitter or hormone that binds to receptors on smooth muscle plasma membranes determines the response of the muscle.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inflammation of the fibrous connective tissue resulting in stiffness and soreness is
A) cramps.
B) fibrositis.
C) fibrosis.
D) muscular dystrophy.
E) paralysis.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
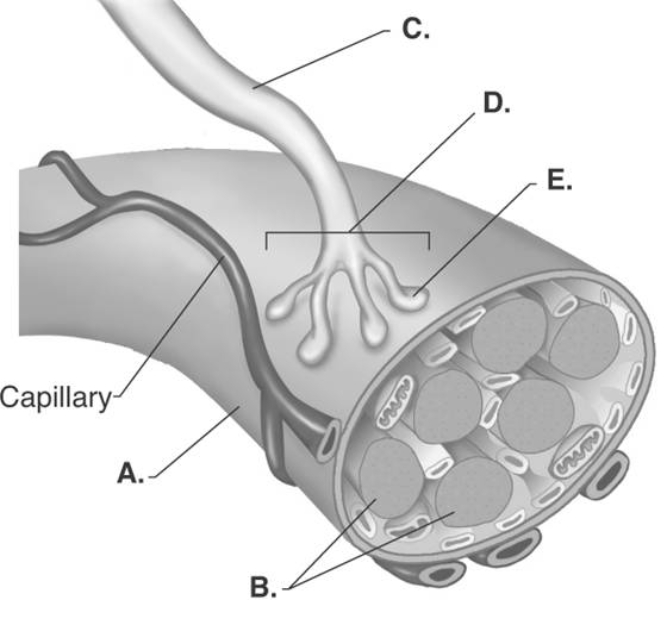 -The figure illustrates the neuromuscular junction. What does "E" represent?
-The figure illustrates the neuromuscular junction. What does "E" represent?
A) presynaptic terminal
B) muscle fiber
C) neuromuscular junction
D) axon branch
E) myofibrils
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs during recovery from oxygen deficit?
A) an elevated level of anaerobic metabolism
B) depletion of reserves of creatine phosphate
C) conversion of excess lactic acid to glucose
D) glycogen degradation to provide creatine
E) depressed level of aerobic respiration
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Synaptic vesicles in the neuromuscular junction contain
A) calcium.
B) ATP.
C) acetylcholine.
D) acetylcholinesterase.
E) sodium.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of respiration occurs in the mitochondria?
A) anaerobic respiration
B) aerobic respiration
C) both anaerobic and aerobic respiration
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 194
Related Exams