A) chromatid
B) proteins
C) chromosome
D) centromere
E) chromatin
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell can meet increased energy demands by an increase in
A) its overall size so it has more room to generate energy.
B) the number of mitochondria.
C) lysosomal enzyme and ribosome activity within the cell.
D) nuclear DNA activity.
E) ribosomal subunits.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular membrane transport process exhibits saturation, uses carrier molecules, but does NOT require ATP. The process is probably
A) active transport.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) pinocytosis.
E) phagocytosis.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Molecules that serve as chemical signals to open or close gated ion channels are
A) isotopes.
B) ligands.
C) responders.
D) communicators.
E) membrane potentials.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What term dealing with cancer means "not inclined to spread or become worse'?
A) metastasis
B) malignant
C) sarcoma
D) benign
E) carcinoma
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events occurs in the nucleus?
A) ATP synthesis
B) ribosomal proteins formed
C) chromatin condenses to form chromosomes
D) manufacture of phospholipids
E) None of these events occurs in the nucleus.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
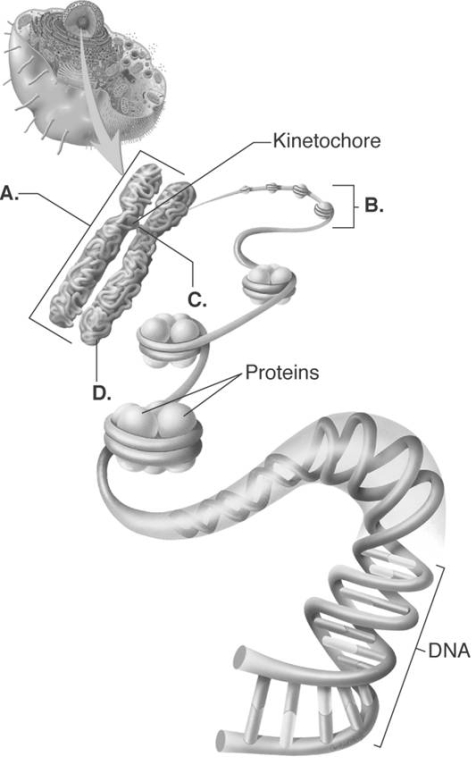 -Answer these questions about chromosome structure. What does "B" represent?
-Answer these questions about chromosome structure. What does "B" represent?
A) chromatid
B) proteins
C) chromosome
D) centromere
E) chromatin
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would increase the maximum rate of facilitated diffusion?
A) increase the concentration gradient of the transported molecule to the saturation point
B) decrease the concentration gradient of the transported molecule
C) increase the concentration of the competitive molecules
D) increased ATP synthesis
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cilia and flagella are distinguished from each other on the basis of
A) width and numbers.
B) length and numbers.
C) depth and numbers.
D) length and width.
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells produce and respond to chemical and electrical signals as a means of
A) communicating.
B) metabolizing.
C) reproducing.
D) synthesizing.
E) using energy.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A red blood cell that is placed in a hypertonic solution
A) loses water.
B) gains water.
C) floats.
D) ruptures.
E) neither gains nor loses water.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What organelle packages materials for secretion from the cell?
A) endoplasmic reticulum
B) Golgi apparatus
C) nucleolus
D) peroxisomes
E) flagellum
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cyanide stops the production of ATP. Which of the following processes would be affected?
A) simple diffusion
B) osmosis
C) active transport
D) facilitated diffusion
E) filtration
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a sperm cell comes into contact with an egg cell, there is a change in the electrical charge across the plasma membrane and various channel proteins close. These channels would be called
A) open-gated channels.
B) voltage-gated channels.
C) chemical-gated channels.
D) ligand-gated channels.
E) nongated ion channels.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A mitochondrial disease is passed to offspring via the father.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Channel proteins
A) are binding sites for other molecules.
B) utilize the G protein complex to function.
C) are found only on endoplasmic reticulum.
D) allow cells to recognize one another.
E) provide a tunnel through which ions or molecules can enter or leave the cell.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cytoskeleton consists of
A) lipochromes, microfilaments, and microtubules.
B) actin filaments, mitochondria, and intermediate filaments.
C) microfilaments, mitochondria, and lipochromes.
D) microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments.
E) ribosomes, the nucleus, and the Golgi apparatus.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
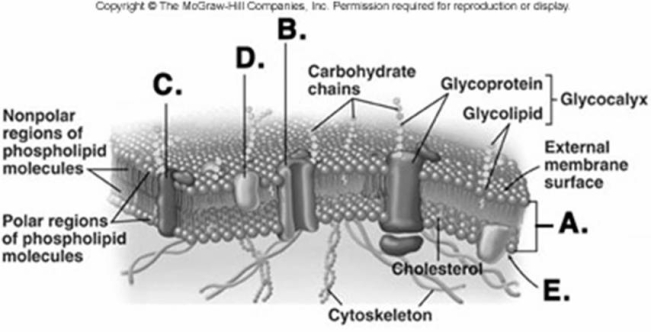 -What structure does "E" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
-What structure does "E" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
A) membrane channel protein
B) phospholipid bilayer
C) internal membrane surface
D) peripheral protein
E) receptor protein
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What term dealing with cancer means "spreading to a new site"?
A) metastasis
B) malignant
C) sarcoma
D) benign
E) carcinoma
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The greater the concentration of a solution, the greater the
A) tendency for water to diffuse from the solution.
B) osmotic pressure of the solution.
C) number of carrier molecules present.
D) amount of solvent.
E) rate of facilitated diffusion.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 211
Related Exams