A) storage carbohydrate in animals.
B) storage carbohydrate in plants.
C) nondigestible plant polysaccharide.
D) major nutrient for most body cells.
E) sugar found in RNA.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cellulose is the
A) storage carbohydrate in animals.
B) storage carbohydrate in plants.
C) nondigestible plant polysaccharide.
D) major nutrient for most body cells.
E) sugar found in RNA.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A molecule is
A) a combination of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
B) a positively charged ion.
C) a negatively charged ion.
D) a substance that conducts electricity when placed in solution.
E) an alteration in the three-dimensional structure of a protein.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organic groups does a steroid belong to?
A) carbohydrate
B) protein
C) lipid
D) nucleic acid
E) vitamin
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The energy stored in ATP is a form of ________ energy.
A) mechanical
B) chemical
C) kinetic
D) heat
E) electrical
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organic groups does DNA belong to?
A) carbohydrate
B) protein
C) lipid
D) nucleic acid
E) vitamin
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a function of carbohydrates in the body?
A) structural component of DNA
B) protection
C) bulk in feces
D) energy
E) structural component of RNA
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Denaturation is
A) a combination of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
B) a positively charged ion.
C) a negatively charged ion.
D) a substance that conducts electricity when placed in solution.
E) a change in the three-dimensional structure of a protein.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Heat energy is
A) the form of energy that actually does work.
B) movement of ions or electrons.
C) energy that flows between objects with different temperatures.
D) stored energy that could do work but is not doing so.
E) energy that moves in waves.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
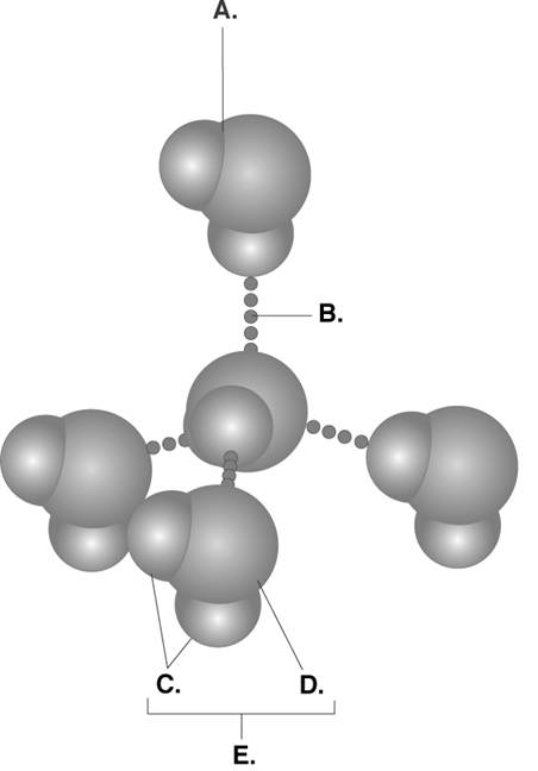 -Water accounts for 50% of the weight of a young adult female and 60% of a young adult male. What kind of molecule is found at "E"?
-Water accounts for 50% of the weight of a young adult female and 60% of a young adult male. What kind of molecule is found at "E"?
A) hydrogen bond
B) water molecule
C) oxygen atom
D) hydrogen atom
E) polar covalent bond
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electrolyte is
A) a combination of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
B) a positively charged ion.
C) a negatively charged ion.
D) a substance that conducts electricity when placed in solution.
E) the alteration in the three-dimensional structure of a protein.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solution that contains one osmole of solute in one kilogram (kg) of water is called a
A) 1% solution.
B) 1 molar solution.
C) 10% solution.
D) 1 osmolal solution.
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a source of nitrogen for the body?
A) carbohydrates
B) water
C) proteins
D) glucose
E) lipids
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The model that helps explain how an enzyme works is the
A) activation model.
B) lock-and-key model.
C) three-dimensional model.
D) denaturation model.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neutral atom will become a cation if it
A) gains electrons.
B) gains protons.
C) loses electrons.
D) loses protons.
E) gains neutrons.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Covalent bonds form when
A) atomic nuclei fuse.
B) molecules become ionized.
C) neutrons are transferred from one atom to another.
D) protons are lost from atoms.
E) electrons are shared between two atoms.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Cobalt-60 is used for radiation treatments of cancer. How many neutrons does an atom of Co-60 have?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The element uranium has a mass number of 238 and contains 92 protons. How many electrons does an atom of uranium have?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Cobalt-60 is used for radiation treatments of cancer. What is the mass number of Co-60?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecule used most frequently by cells as a fuel belongs to which of the following groups?
A) prostaglandins
B) carbohydrates
C) nucleic acids
D) steroids
E) phospholipids
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 155
Related Exams