A) amplitude of the action potential increases.
B) duration of the action potential increases.
C) frequency of occurrence of action potentials increases.
D) resonance of action potentials increases.
E) height of the action potentials increases.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
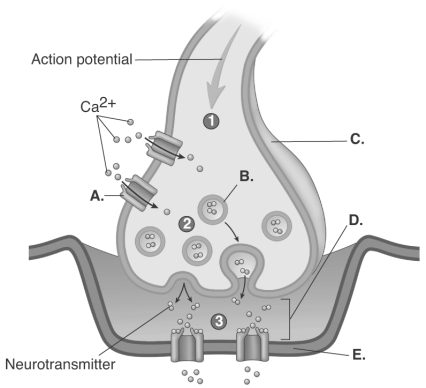 -The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse.What does "D" represent?
-The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse.What does "D" represent?
A) postsynaptic membrane
B) synaptic cleft
C) synaptic vesicle
D) voltage-gated calcium channel
E) presynaptic terminal
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Action potentials are conducted more rapidly when transmission is
A) from node to node on a myelinated axon.
B) on a small diameter axon.
C) on an unmyelinated axon.
D) from internode to internode.
E) from internode to node on a myelinated axon.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) microglia - provide support for the neuron cell body
B) astrocytes - blood-brain barrier
C) oligodendrocytes - form myelin sheaths
D) ependymal cells - produce cerebrospinal fluid
E) ependymal cells - choroid plexus
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Axons
A) contain the nucleus.
B) are numerous extensions from each neuron.
C) do not have a trigger zone.
D) have a distal portion that branches to form the presynaptic terminals.
E) do not have a resting membrane potential.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the neuroglial cell with its function. -Schwann cell
A) influence function of blood-brain barrier
B) macrophages in CNS
C) produce cerebrospinal fluid
D) form myelin sheath around axons in CNS
E) form myelin sheath around part of the axon in the PNS
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the neuroglial cell with its function. -microglia
A) influence function of blood-brain barrier
B) macrophages in CNS
C) produce cerebrospinal fluid
D) form myelin sheath around axons in CNS
E) form myelin sheath around part of the axon in the PNS
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Action potentials are conducted rapidly from one node of Ranvier to the next in a process called ____________ conduction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the resting membrane potential,increasing the sodium ion concentration in the ECF results in
A) hyperpolarization.
B) depolarization.
C) hypopolarization.
D) little change in membrane potential.
E) There is not enough information to determine the results.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a neuroglia of the CNS?
A) ependymal cells
B) satellite cells
C) oligodendrocytes
D) astrocytes
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) central nervous system - brain
B) autonomic nervous system - sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
C) peripheral nervous system - spinal nerves
D) somatic nervous system - sensory division of PNS
E) peripheral nervous system - sensory and motor divisions
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gap junctions are functional __________ synapses.
A) chemical
B) electrical
C) potential
D) intracellular
E) neuromuscular
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Continuous conduction of an action potential means that
A) once one action potential is created,it moves down the axon.
B) the whole axon depolarizes at the same time.
C) one action potential stimulates the production of a new action potential at the adjacent site.
D) an action potential is conducted from one node of Ranvier to the next node.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
____________ are processes that conduct electric signals toward the cell body.
Correct Answer

verified
dendrites
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The central nervous system includes the
A) ganglia.
B) spinal cord.
C) spinal nerves.
D) cranial nerves.
E) sensory receptors.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following concerning concentration differences across the plasma membrane. -postassium ions
A) concentration of potassium
B) concentration of sodium and chloride
C) negatively charged proteins
D) sodium/potassium pump
E) plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During depolarization of the plasma membrane,
A) sodium ions move rapidly into the cell.
B) potassium ions move rapidly out of the cell.
C) membrane permeability to sodium ions decreases.
D) the outside of the cell becomes positively charged relative to the inside.
E) sodium ions move rapidly out of the cell.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO inhibitors)
A) prevent synaptic transmission.
B) enhance the breakdown of norepinephrine.
C) enhance the binding of norepinephrine to its receptors.
D) prevent the release of norepinephrine by the presynaptic terminal.
E) have no effect on the action of norepinephrine.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
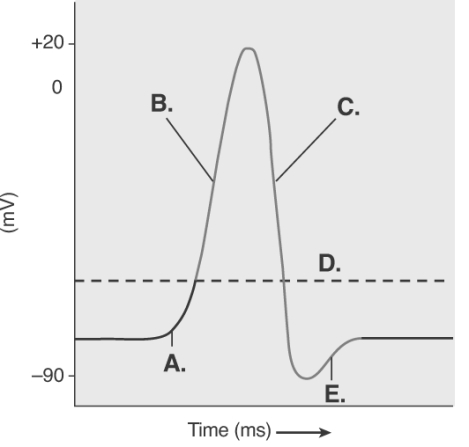 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "C" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "C" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The peripheral nervous system includes the
A) brain.
B) spinal cord.
C) cranial nerves.
D) blood-brain barrier.
E) cerebellum.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 155
Related Exams