A) action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
B) a muscle produces constant tension during contraction.
C) a muscle produces an increasing tension during contraction.
D) a muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
E) a muscle produces tension,but the length of the muscle is increasing.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hypertrophy of skeletal muscles from weight lifting is caused by an increase in the
A) number of muscle fibers.
B) size of muscle fibers.
C) number of striations.
D) number of nuclei within the muscle fibers.
E) number of muscle cells.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myosin is also known as the
A) thick myofilament.
B) thin myofilament.
C) intermediate myofilament.
D) short myofilament.
E) sarcomere.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen deficit represents
A) the amount anaerobic metabolism must increase after exercise.
B) the amount of oxygen converted to lactic acid during exercise.
C) the amount of carbon dioxide that cells need to eliminate.
D) conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid.
E) the amount of oxygen that cells need to replenish ATP supplies after exercise.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
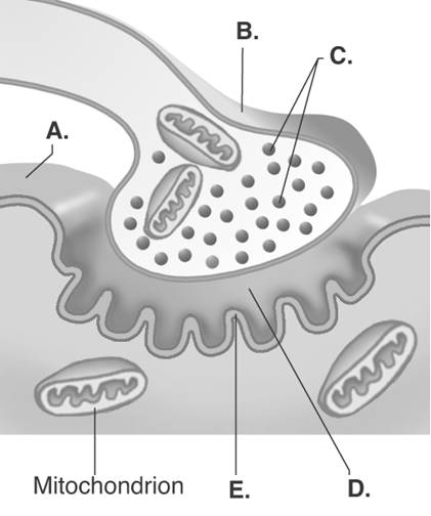 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "A" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "A" represent?
A) synaptic vesicles
B) synaptic cleft
C) sarcolemma
D) presynaptic terminal
E) postsynaptic membrane
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whole muscles can respond in a graded fashion to stimuli by varying
A) the force of contraction of individual muscle fibers.
B) the number of motor units recruited.
C) the amplitude of the action potential.
D) the frequency of stimulus.
E) thresholds.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A concentric contraction is described as
A) action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
B) a muscle produces constant tension during contraction.
C) a muscle produces an increasing tension during contraction.
D) a muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
E) a muscle produces tension,but the length of the muscle is increasing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue has spindle-shaped cells?
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
D) both skeletal and cardiac muscle
E) both cardiac and smooth muscle
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time between application of the stimulus to a motor neuron and the beginning of contraction is called the _____ phase.
A) contraction
B) relaxation
C) latent or lag
D) refractory
E) threshold
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would contribute to muscular fatigue in the muscle fiber?
A) the emotional state of an individual
B) depletion of ATP reserves
C) inability of the motor neuron to produce sufficient quantities of acetylcholine
D) depletion of neurotransmitter
E) blocked receptors in the postsynaptic membrane
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a property of the myosin head?
A) They form cross-bridges with the active sites of actin.
B) They have a hinge region to bend and straighten.
C) They bind to troponin.
D) They have ATPase activity.
E) They bind to ATP.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for muscle relaxation to occur,
A) calcium ions must be transported to troponin.
B) power strokes slow down.
C) the active sites on actin must be blocked.
D) sodium ions must be actively transported to troponin.
E) the active sites on myosin must be uncovered.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) The greater the overlap of actin and myosin,the stronger the contraction.
B) Overstretching a muscle will increase its tension.
C) Optimal actin and myosin overlap will produce maximal contraction.
D) The greatest amount of tension is achieved when actin and myosin do not overlap.
E) Tension is great when actin and myosin overlap as much as they can.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intense exercise that results in a great deal of anaerobic activity
A) converts some slow-twitch fibers into fast-twitch fibers.
B) increases muscular strength and mass.
C) enlarges slow-twitch fibers.
D) decreases the efficiency of fast-twitch fibers.
E) decreases muscle strength and mass.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Too much acetylcholinesterase causes
A) continuous stimulation of the muscle fiber.
B) rapid degradation of acetycholine.
C) voltage-gated calcium ion channels opening in the presynaptic terminal.
D) an increase in sodium uptake by the muscle fiber.
E) exocytosis of synaptic vesicles.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true of the latch state of smooth muscle contraction?
A) Myosin phosphatase removes the phosphate group from myosin.
B) It explains why smooth muscle can sustain tension for long periods of time.
C) It occurs when the phosphate is removed while the cross-bridges are attached to actin.
D) It occurs when the phosphate is removed while the cross-bridges are not attached to actin.
E) It allows contraction without a large energy expenditure.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tetanus of a muscle is thought to be caused by
A) high calcium ion concentrations in the sarcoplasm.
B) the rapid movement of sodium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) an increase in stimulus strength.
D) increased temperature in the active muscle.
E) decreased amounts of calcium ions in muscle tissue.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In smooth muscle,most of the calcium needed for muscle contraction
A) is in the dense bodies.
B) enters from extracellular fluid.
C) is attached to the intermediate filaments.
D) must be activated by myosin kinase.
E) is stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Channels that open or close in response to changes in the electrical charge or voltage across the plasma membrane are called
A) ligand-gated ion channels.
B) leak ion channels.
C) relegated ion channels.
D) voltage-gated ion channels.
E) obligated ion channels.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myosin phosphatase
A) activates myosin kinase.
B) forms the cross-bridge.
C) removes phosphate from myosin.
D) binds to calcium-calmodulin complex.
E) opens calcium channels.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 189
Related Exams