A) Triton, a moon of Neptune
B) Io, a moon of Jupiter
C) Titan, a moon of Saturn
D) Earth's Moon
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Earth experiences an equinox when the day and night are of equal length everywhere on the planet. Does Uranus experience an equinox? If so, how often? (The orbital period of Uranus is 84 years.)
A) No.
B) Yes, every 6 months just like Earth.
C) Yes, every 42 years.
D) Yes, every 84 years.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the largest planetary satellite in the solar system?
A) Earth's Moon
B) Neptune's satellite Triton
C) Jupiter's satellite Ganymede
D) Saturn's satellite Titan
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The required heating of the large Galilean moon Io of Jupiter in order to produce volcanic activity is probably caused by
A) tidal distortion by Jupiter and its other moons.
B) its original heat of formation.
C) nuclear fission within its interior.
D) radioactive elements in its surface.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the only satellite in the solar system known to possess a permanent, dense atmosphere?
A) Titan
B) Charon
C) Callisto
D) Ganymede
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For how long has it been known that the planet Jupiter has moons?
A) since the first spacecraft flybys by Pioneer I in 1979
B) since 1948, when the Mount Palomar telescope was completed
C) since Galileo turned his telescope toward the sky in 1610
D) since the time of the ancient Greeks
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What were the results of the impacts of the fragments of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 into Jupiter?
A) Holes punched through the clouds, and craters gouged Jupiter's surface.
B) There were essentially no visible effects because the fragments plummeted deep below the cloud layers before being destroyed.
C) Rings of debris were flung into orbit around Jupiter's equator.
D) Fireballs hotter than the Sun's surface made dark splotches that lasted for months.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the moons of the giant planets is known to have a significant and dense atmosphere?
A) Europa, a moon of Jupiter
B) Titan, a moon of Saturn
C) Triton, a moon of Neptune
D) Io, a moon of Jupiter
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of these features has NOT been found on Enceladus?
A) jets of ice water shooting into the atmosphere
B) a uniformly and heavily cratered surface
C) stripes of recently formed material
D) a magnetic field
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pattern followed by the average densities of the Galilean moons of Jupiter with increasing distance from the planet?
A) Average density increases with distance from the planet.
B) Average density shows no pattern with distance; the highest-density moon is Ganymede, the largest moon.
C) Average density is the same for all moons because they were made from the same material.
D) Average density decreases with distance from the planet.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What appears to be the origin of the light, grooved terrain on the surface of Ganymede?
A) impacts by cometary debris
B) cracking of the surface caused by shrinkage of the moon as it cooled
C) cracking of the icy surface, releasing water that expanded as it froze into ice
D) flow of water on the solid surface of the moon at some time in the past, which subsequently shrank as it froze into this distinctive terrain
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Seasonal variations over a full Uranian year at a particular point on Uranus would
A) not be present at any point on the planet because dense clouds shield it from climate changes.
B) be nonexistent because such variations at any point on the planet will be smoothed out during its long "year" by the planet's rapid rotation.
C) be almost nonexistent because Uranus moves in an almost perfectly circular orbit and its distance from the Sun remains constant.
D) be extreme because its spin axis is nearly in its orbital plane.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which chemical or chemicals appear to play a prominent role in the "volcanoes" of Io?
A) water and steam
B) molten lava
C) methane and ammonia
D) sulfur and sulfur dioxide
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these objects rotates the MOST quickly around its own axis?
A) Venus
B) Earth's Moon
C) Earth
D) Jupiter
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Callisto, the outer Galilean moon of Jupiter, has a surface consisting of
A) an icy crust showing two interlocking types of terrain, one ancient and heavily cratered, the other younger with systems of parallel grooves.
B) rock, heavily cratered like the highlands of Earth's Moon.
C) a relatively young, icy crust covered with a network of streaks and cracks and only a few impact craters.
D) a very dark and ancient icy crust covered with numerous craters, with no surface cracks or groove belts that would indicate internal activity.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-7 shows the three cloud layers of Jupiter and Saturn. What is the unlabeled blank space beneath these layers? 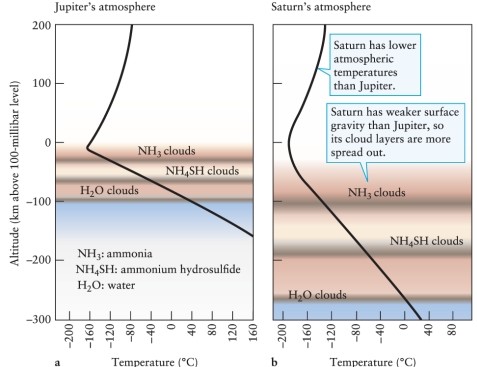
A) gaseous hydrogen
B) liquid hydrogen
C) solid metallic hydrogen
D) Rocks
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The predominant large-scale atmospheric circulation pattern on Jupiter is characterized by
A) strong winds blowing eastward at all latitudes so that the entire atmosphere rotates faster than the planet.
B) isolated cyclones (low-pressure areas) and anticyclones (high-pressure areas) , similar to those on Earth.
C) strong winds blowing parallel to the equator but in opposite directions at different latitudes.
D) strong winds blowing westward at all latitudes so that the entire atmosphere rotates more slowly than the planet.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which satellite of Jupiter is volcanically active?
A) Europa
B) Io
C) Callisto
D) Ganymede
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on its average density of 2970 kg/m3 compared with that of water at 1000 kg/m3, what is the internal structure of Jupiter's moon Europa thought to be?
A) almost entirely water in liquid form or as ice
B) large iron core, the rest rock
C) half rock, half water and ice
D) a metallic core of high density with one-quarter of its mass composed of water and ice
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Io passes between Jupiter and Europa, both moons experience gravitational stress. On Europa this is responsible for three of the features listed below. Which feature does NOT occur as a result of the gravitational flexing of Europa?
A) cracks on the surface
B) heat to keep subsurface water liquid
C) water geysers
D) lava/sulfur volcanoes
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 301 - 320 of 360
Related Exams