A) femoral nerve and the tibial nerve.
B) tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve.
C) femoral nerve and the obturator nerve.
D) common fibular nerve and the pudendal nerve.
E) superior gluteal and inferior gluteal.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The perineurium
A) surrounds nerve cell bodies.
B) surrounds individual axons and their Schwann cells.
C) bundles axons into fascicles.
D) bundles fascicles into nerves.
E) bundles fascicles into axons.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If reciprocal innervation failed during a stretch reflex, the consequence might be that
A) the overall movement would be diminished due to opposing muscles contracting simultaneously.
B) the overall movement would be exaggerated due to the lack of regulation from opposing muscle contraction.
C) the complete loss of movement due to lack of stimulation of the effector muscle.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Myelin is essentially the endoneurium of myelinated axons.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The thickest of the meninges is the ________.
A) pia mater
B) arachnoid mater
C) subdural space
D) subarachnoid space
E) dura mater
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adduction of the thigh involves the ________ nerve.
A) peroneal
B) femoral
C) obturator
D) pudendal
E) tibial
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the nerve or plexus with its appropriate description. -Tibial nerve
A) Innervates the iliopsoas, sartorius, and quadriceps femoris
B) Innervates muscles of the pelvic floor
C) Innervates the muscles that adduct the thigh
D) Innervates the anterior and lateral muscles of the leg
E) Branches to form the medial and lateral plantar nerves
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spinal cord begins at the ________.
A) cerebellum
B) medulla oblongata
C) foramen magnum
D) conus medullaris
E) 1st cervical vertebrae
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The ________ is the basic functional unit of the nervous system and is capable of receiving a stimulus and producing a response.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the action with the specific reflex. -Allows for the coordinated contraction and relaxation of opposing muscle groups
A) Stretch reflex
B) Golgi tendon reflex
C) Withdrawal reflex
D) Crossed extensor reflex
E) Reciprocal innervation
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You go to the movies after a long day and you begin to nod off as soon as the movie starts. Your head starts to lower a little, but a reflex causes your head to rise. This is called the ________ reflex.
A) tendon
B) crossed extension
C) withdrawal
D) stretch
E) flexor (withdrawal)
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reflex that prevents excessive tension in a muscle is the ________ reflex.
A) stretch
B) withdrawal
C) Golgi tendon
D) reciprocal
E) crossed extensor
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A man was in an accident during which his spinal cord was severed between C6 and C7. Which of the following would NOT be a consequence of this injury?
A) Loss of sensation in the trunk below the shoulders, the lower limbs, and portions of the arms
B) Loss of use of the phrenic nerves and paralysis of the diaphragm
C) Loss of movement in the lower limbs
D) Loss of the use of the intercostals nerves, and breathing would be affected because the intercostals muscles would be paralyzed
E) Loss of touch sensation on the lower lumbar region.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Structurally, the simplest reflex is the ________.
A) stretch reflex
B) Golgi tendon reflex
C) reciprocal reflex
D) alternating reflex
E) withdrawal reflex
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Doctor Johansson wants to test a patient's reflexes by briskly striking the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer. Which reflex is Dr. Johansson testing?
A) Golgi tendon reflex
B) Withdrawal reflex
C) Knee-jerk reflex
D) Crossed extensor reflex
E) Reciprocal innervation
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cross-sectional view of the spinal cord reveals white matter on the
A) inside, gray matter on the outside, and a dorsal motor root.
B) outside, gray matter on the inside, and a ventral motor root.
C) inside, gray matter on the outside, and a dorsal sensory root.
D) outside, gray matter on the inside, and a ventral sensory root.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following sensory functions involves neurons in the dorsal root ganglion?
A) Smell
B) Hearing
C) Touch
D) Taste
E) Vision
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where is cerebrospinal fluid found around the spinal cord?
A) Subdural space
B) Epidural space
C) Thecal sac
D) Subarachnoid space
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reflexes
A) are homeostatic.
B) are not homeostatic.
C) are voluntary conscious responses to a stimulus.
D) are integrated in the spinal cord, but not the brain.
E) are integrated in the brain, but not the spinal cord.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
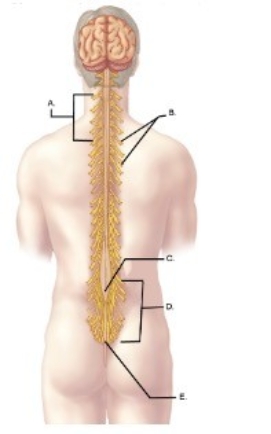 -What does "A" represent?
-What does "A" represent?
A) Spinal nerves
B) Conus medullaris
C) Cervical enlargement
D) Filium terminale
E) Cauda equina
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 141
Related Exams