A) ganglia
B) spinal cord
C) spinal nerves
D) cranial nerves
E) sensory receptors
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blood-brain barrier
A) permits passage of foreign substances from the blood to the neurons.
B) prohibits the transport of amino acids and glucose to the neurons.
C) prohibits the removal of waste materials from the neurons.
D) protects neurons from toxic substances in the blood.
E) does not prevent fluctuations in the composition of the blood from affecting the functions of the brain.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) Central nervous system - brain
B) Autonomic nervous system - sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
C) Peripheral nervous system - spinal nerves
D) Somatic nervous system - sensory division of PNS
E) Peripheral nervous system - sensory and motor divisions
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The absolute refractory period assures
A) prolonged depolarization during the action potential.
B) completion of repolarization before another action potential.
C) that no after-potential occurs.
D) reversal of the direction of propagation of the action potential.
E) that the stimulus is strong enough to elicit a response.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Groups of related nerve cell bodies located outside of the central nervous system are called ________.
A) ganglia
B) plexus
C) tracts
D) nerves
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Synapses in which gap junctions allow ions to diffuse quickly from cell to cell are called ________ synapses.
A) electrical
B) chemical
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nervous system
A) monitors internal and external stimuli.
B) transmits information in the form of action potentials.
C) interprets or assesses information.
D) maintains homeostasis.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a glial cell of the CNS?
A) Ependymal cells
B) Satellite cells
C) Oligodendrocytes
D) Astrocytes
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gap junctions are functionally ________ synapses.
A) chemical
B) electrical
C) potential
D) intracellular
E) neuromuscular
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
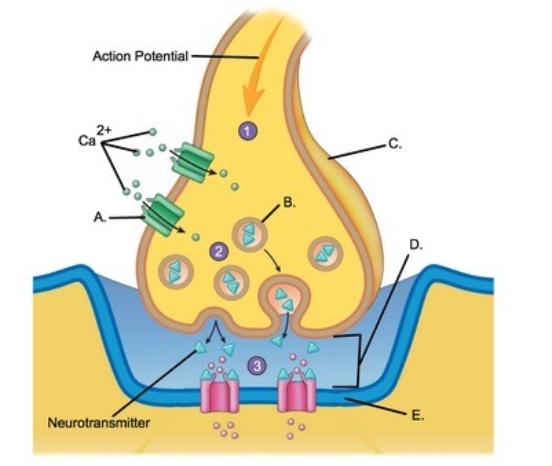 -Identify structure "B" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) Neuron cell body (soma)
D) Dendrites
E) Axon
-Identify structure "B" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) Neuron cell body (soma)
D) Dendrites
E) Axon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Action potentials are conducted more rapidly when transmission is
A) from node to node on a myelinated axon.
B) on a small diameter axon.
C) on an unmyelinated axon.
D) from internode to internode.
E) from internode to node on a myelinated axon.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the absolute refractory period, the cell
A) generates many local potentials.
B) is insensitive to further stimulation.
C) responds to even weak stimuli.
D) reverses the direction of the action potential.
E) is very sensitive.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The nervous system and the endocrine system are the major control systems of the body.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Most pseudo-unipolar neurons are ________ neurons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Voltage-gated Na+ channels are sensitive to changes in the extracellular concentration of ________.
A) K+
B) proteins
C) Na+
D) Cl−
E) Ca2+
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptor molecules
A) are nonspecific.
B) are always lipids.
C) attach to the synaptic cleft.
D) determine whether a neurotransmitter will be excitatory or inhibitory.
E) are not attached to ligand-gated channels.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Clusters of gray matter deep within the brain are called ________.
A) cortices
B) nerves
C) ganglia
D) nuclei
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a neurotransmitter binds to its receptor and increases the permeability of the postsynaptic membrane to Na+,
A) the membrane will be hyperpolarized.
B) more Cl− will also diffuse into the cell.
C) an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) will result.
D) the membrane will become impermeable to K+.
E) Na+ diffuses out of the cell.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The autonomic nervous system
A) stimulates skeletal muscle contractions.
B) has two sets of neurons in a series.
C) is involved in problem solving.
D) is under voluntary control.
E) does not include the central nervous system.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Local hyperpolarization in a synapse is called a/an ________.
A) excitatory postsynaptic potential
B) resting membrane potential
C) inhibitory postsynaptic potential
D) gap junction potential
E) action potential
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 192
Related Exams