A) It is irreversible.
B) It can be caused by disuse.
C) It can be caused by denervation.
D) Transcutaneous stimulation can help prevent it.
E) Muscle fibers are replaced by connective tissue.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myasthenia gravis results from the destruction of acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction, but treatment involves medications that reduce acetylcholinesterase activity. Which statement best explains the effectiveness of these medications?
A) The antibodies destroy some but not all of the acetylcholine receptors, so reducing acetylcholinesterase activity increases the likelihood that acetylcholine will bind to the remaining receptors.
B) Acetylcholinesterase is the substance that destroys the receptors as well, so reducing its activity increases the number of acetylcholine receptors.
C) Acetylcholinesterase breaks down the acetylcholine to a substance that can bind to the damaged receptors.
D) The antibodies that destroy the acetylcholine receptors are less likely to work if acetylcholinesterase is present.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
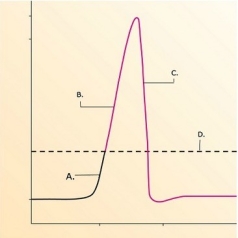 -What does "C" represent on the diagram?
-What does "C" represent on the diagram?
A) Threshold
B) Depolarization
C) Depolarization phase of action potential
D) Repolarization phase of action potential
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If one nerve stimulus arrives at a muscle fiber so soon that the fiber has only partially relaxed from the previous twitch, the most likely result will be ________.
A) fatigue
B) spasm
C) incomplete tetanus
D) complete tetanus
E) flaccid paralysis
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A myofibril is the
A) plasma membrane of a muscle fiber.
B) cytoplasm of a muscle fiber.
C) structural and functional unit of the skeletal muscle fiber.
D) contractile thread that extends the length of the muscle fiber.
E) protein strand composed of actin.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ATPase is found in
A) F-actin strands.
B) G-actin globular units.
C) myosin heads.
D) tropomyosin grooves.
E) troponin molecules.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A lack of glycolytic enzymes within skeletal muscle fibers would impair which type of ATP-yielding process?
A) Anaerobic respiration
B) Aerobic respiration
C) Both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration are correct.
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following list of biochemical events in the correct sequence. (1) An action potential is conducted deep into the muscle fiber by the T tubule. (2) Calcium ions bind to troponin. (3) The membranes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum become more permeable to calcium ions. (4) Calcium ions diffuse into the sarcoplasm around the myofibril. (5) The troponin-tropomyosin complex moves exposing active sites.
A) 1, 5, 2, 3, 4
B) 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
C) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
D) 1, 3, 2, 5, 4
E) 1, 4, 3, 2, 5
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A skeletal muscle generates the greatest tension when it is
A) greatly stretched before being stimulated.
B) partially stretched before being stimulated.
C) fully relaxed before being stimulated.
D) well-rested and low in creatine phosphate.
E) high in lactate concentration.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following descriptions best represents the appearance of the sarcomere during peak contraction?
A) The H zone is eliminated, and the I bands are very thin.
B) The width of the A band is slightly less than the width of the I band.
C) The H zone is equivalent to one-third of the length of the A band.
D) The I bands and A bands are of equal widths.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What does "D" represent on the diagram?
-What does "D" represent on the diagram?
A) Threshold
B) Depolarization
C) Depolarization phase of action potential
D) Repolarization phase of action potential
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skeletal muscle fibers
A) possess striations.
B) can contract but are not extensible or excitable.
C) do not require nerve innervation to contract.
D) increase dramatically in number after birth.
E) are found in the walls of the stomach.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In excitation-contraction coupling,
A) Ca2+ must bind with myosin to expose active sites on actin.
B) myosin heads bind to exposed active sites on actin.
C) cross-bridges form between myosin heads and Ca2+.
D) movement of the troponin-tropomyosin complex causes actin myofilaments to slide.
E) ATP binds to actin myofilaments.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the statement concerning general functional characteristics of muscle that is true.
A) Muscle tissue shortens forcefully but lengthens passively.
B) Muscle tissue shortens passively but lengthens forcefully.
C) Muscle tissue can get shorter, but cannot get longer.
D) Muscle tissue can get longer, but cannot get shorter.
E) None of these statements are true.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The elevated oxygen consumption relative to activity level after exercise has ended is called
A) oxygen deficit.
B) oxygen debt.
C) oxygen repayment.
D) excess post-exercise oxygen consumption.
E) anaerobic recovery.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
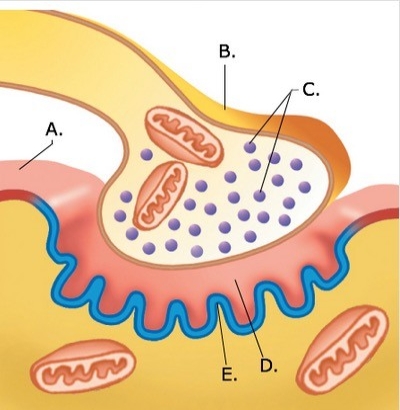 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "B" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "B" represent?
A) Synaptic vesicles
B) Synaptic cleft
C) Sarcolemma
D) Presynaptic terminal
E) Postsynaptic membrane
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Curare blocks acetylcholine receptors at the motor end plate. This would result in
A) increased stimulation of the muscle.
B) more acetylcholinesterase production.
C) lack of Ca2+ uptake by the muscle fiber.
D) inability of the muscle fiber to respond to nervous stimulation.
E) sustained contraction of the muscle.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One ATP molecule is required for
A) formation of the cross-bridge.
B) movement of the cross-bridge.
C) release of the cross-bridge.
D) formation of the cross-bridge and for movement of the cross-bridge.
E) formation of the cross-bridge, for movement of the cross-bridge, and for release of the cross-bridge.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skeletal muscle develops from cells called
A) fascicles.
B) myoblasts.
C) myofibrils.
D) myotomes.
E) fasciculi.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best predicts the effect of a substance that blocks creatine kinase activity?
A) ATP production from creatine phosphate would decrease.
B) ATP production from creatine phosphate would increase.
C) ADP production from creatine phosphate would decrease.
D) ADP production from creatine phosphate would increase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 231
Related Exams