A) produces ATP molecules faster than anaerobic respiration.
B) yields as many as 36 ATP per glucose molecule metabolized.
C) occurs whether oxygen is present or not.
D) occurs entirely in the cytoplasm.
E) occurs in the ribosomes.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The refractory period
A) is the time during which the tissue cannot respond again.
B) results in complete and incomplete tetanus.
C) is the condition in which the muscle fiber only partially relaxes between contractions.
D) is the condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations.
E) is the constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following connective tissue layers is outside all the others?
A) Perimysium
B) Endomysium
C) Epimysium
D) Paramysium
E) Sarcolemma
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following individuals would have more mitochondria in her skeletal muscle?
A) A 50-year-old sedentary computer programmer
B) A 22-year-old soccer player
C) A long-term hospice patient
D) A model on a reduced-calorie diet
E) A newborn
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for excitation-contraction coupling to occur, the production of an action potential must occur within the ________ of a muscle fiber.
A) contraction
B) junction
C) sarcolemma
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue possesses striations?
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Smooth muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
D) Both skeletal and cardiac muscle are correct.
E) Both cardiac and smooth muscle are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes titin's roles in muscle contraction? (Check all that apply.)
A) Accounts for muscle's excitability
B) Accounts for muscle's extensibility and elasticity
C) Allows the sarcomere to recoil and stretch
D) Helps to hold the actin myofilaments in position
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alex is participating in a 50-meter dash. Predict the most important chemical process his muscles will rely on during this race.
A) Aerobic respiration
B) Anaerobic respiration
C) Creatine phosphate breakdown
D) Nuclear reactions
E) Both anaerobic respiration and creatine phosphate breakdown are correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
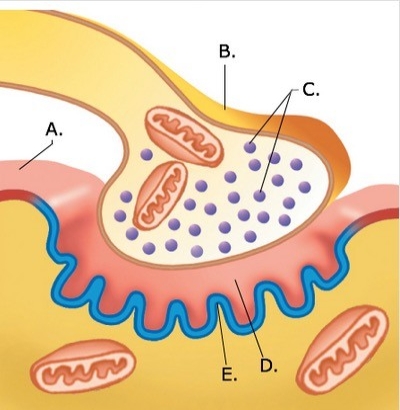 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "A" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "A" represent?
A) Synaptic vesicles
B) Synaptic cleft
C) Sarcolemma
D) Presynaptic terminal
E) Postsynaptic membrane
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sustained muscle contraction is known as ________.
A) tetanus
B) tone
C) treppe
D) twitch
E) paralysis
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning fast-twitch muscle fibers is true?
A) They split ATP rapidly.
B) They have large deposits of myoglobin.
C) They are well adapted to aerobic metabolism.
D) They have a well-developed blood supply.
E) They have many mitochondria.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A proper definition of muscle tone is
A) constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.
B) a feeling of well-being following exercise.
C) the ability of a muscle to maintain a contraction against an outside force.
D) muscles contracting together.
E) warm-up of muscle tissue.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true of the latch state of smooth muscle contraction?
A) Myosin phosphatase removes the phosphate group from myosin.
B) It explains why smooth muscle can sustain tension for long periods of time.
C) It occurs when the phosphate is removed while the cross-bridges are attached to actin.
D) It occurs when the phosphate is removed while the cross-bridges are not attached to actin.
E) It allows contraction without a large energy expenditure.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A volleyball player depends on the gastrocnemius muscles for plantar flexion, whereas a marathon runner depends more on the soleus muscles for the same action. What characteristic of the soleus muscles makes this so?
A) They have smaller mitochondria.
B) They have more glycogen in them.
C) They don't have as many blood capillaries per gram of tissue.
D) They make more use of aerobic respiration.
E) They break ATP down to ADP and Pi faster.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myosin is also known as the
A) thick myofilament.
B) thin myofilament.
C) intermediate myofilament.
D) short myofilament.
E) sarcomere.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hypertrophy of skeletal muscles from weight lifting is caused by an increase in the
A) number of muscle fibers.
B) size of muscle fibers.
C) number of striations.
D) number of nuclei within the muscle fibers.
E) number of muscle cells.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) The greater the overlap of actin and myosin, the stronger the contraction.
B) Overstretching a muscle will increase its tension.
C) Optimal actin and myosin overlap will produce maximal contraction.
D) The greatest amount of tension is achieved when actin and myosin do not overlap.
E) Tension is great when actin and myosin overlap as much as they can.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A muscle fiber will respond to a stimulus when that stimulus reaches the ________ level.
A) threshold
B) relaxation
C) rigor mortis
D) recruitment
E) resting
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aerobic exercise
A) increases vascularity of muscle.
B) develops fatigue-resistant fast-twitch fibers.
C) can increase the efficiency of slow-twitch fibers.
D) can increase the number of mitochondria in muscle fibers.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
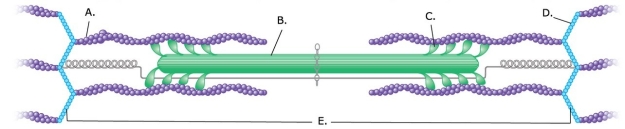 -What does "A" represent on the diagram?
-What does "A" represent on the diagram?
A) Myosin myofilament
B) Actin myofilament
C) Sarcomere
D) Z disk
E) Cross-bridge
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 231
Related Exams