A) Proteosomes
B) Peroxisomes
C) Mitochondria
D) Centrioles
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mitochondria
A) contains DNA.
B) have inner and outer membranes.
C) have inner folds called cristae.
D) are the cell's power plants.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
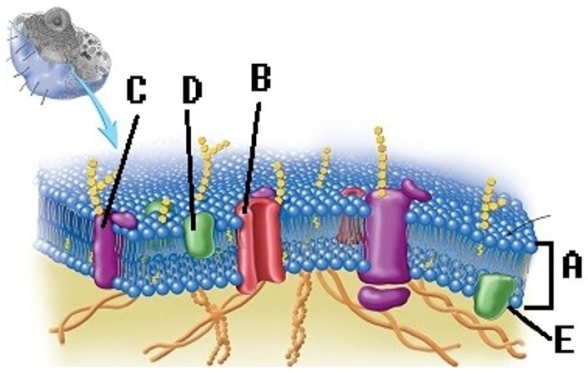 -What structure does "A" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
-What structure does "A" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
A) Membrane channel protein
B) Phospholipid bilayer
C) Internal membrane surface
D) Peripheral protein
E) Integral protein
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell uses centrioles in the process of
A) cell division.
B) energy generation.
C) protein synthesis.
D) RNA replication.
E) nuclear centering.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of cell has abundant mitochondria?
A) White blood cell, a phagocyte
B) Mucus cell (secretes mucus)
C) Liver cells that detoxify hydrogen peroxide
D) Cardiac muscle cells (require large amounts of ATP)
E) Fibroblast (makes protein fibers)
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A symporter will transport ________ across the plasma membrane.
A) two different ions or molecules in opposite directions
B) two different ions or molecules in the same direction
C) two of the same ions or molecules in the same direction
D) one specific ion or molecule
E) two of the same ions or molecules in opposite directions
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the most current model of the plasma membrane,
A) cholesterol forms the innermost layer of the membrane.
B) proteins are free to move about within a double layer of phospholipids.
C) phospholipids and cholesterol form a single lipid bilayer.
D) the membrane is a rigid unchanging structure.
E) the membrane is impermeable to all other molecules.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vitamin A, a fat-soluble vitamin, would move across the plasma membrane into the cell
A) in vesicles.
B) through vitamin membrane channels.
C) by dissolving in the lipid bilayer.
D) by transport with carrier molecules.
E) by active transport.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Communication between cells occurs when chemical messengers from one cell bind to ________ on another cell.
A) channel proteins
B) receptor proteins
C) marker molecules
D) second messengers
E) integrins
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sequence of nucleotides in a messenger RNA molecule is needed to determine the sequence of
A) nucleotides in a gene.
B) amino acids in a protein.
C) nucleotides in the anticodons of tRNA.
D) codons in DNA.
E) amino acids in DNA.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the sequence of the following events in a cell after exposure of the cell to a chemical signal. (1) Increased synthesis of a protein (2) The chemical signal combined with a cytoplasmic receptor (3) An increase in the nuclear concentration of the chemical (4) An increase in mRNA synthesis (5) Genes are activated
A) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4
B) 2, 4, 5, 3, 2
C) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
D) 2, 3, 4, 5, 1
E) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cytoskeleton consists of
A) lipochromes, microfilaments, and microtubules.
B) actin filaments, mitochondria, and intermediate filaments.
C) microfilaments, mitochondria, and lipochromes.
D) microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments.
E) ribosomes, the nucleus, and the Golgi apparatus.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
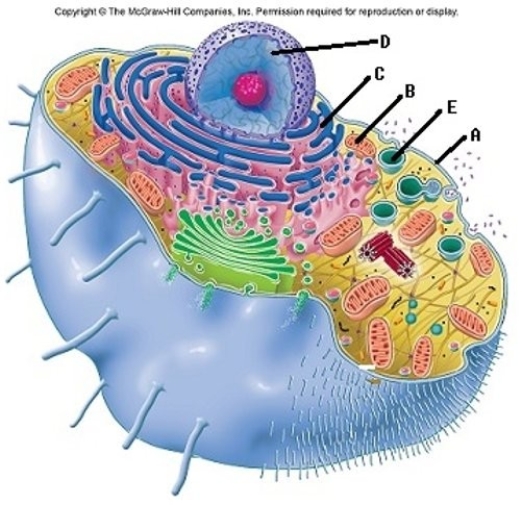 -The cell is the basic unit of life. All cellular structures exhibit special functions. Match the structure with its function. What is the function of "C"?
-The cell is the basic unit of life. All cellular structures exhibit special functions. Match the structure with its function. What is the function of "C"?
A) Directs cellular activities, contains DNA
B) Contains digestive enzymes
C) Outer boundary of cell, controls entry and exit of substances
D) Major site of ATP synthesis when oxygen is available
E) Site of protein synthesis
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which mature cells do not have a nucleus?
A) Columnar cells of upper respiratory tract
B) Sperm cells
C) Columnar cells of small intestines
D) Red blood cells
E) Macrophages (large, mobile white blood cells)
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The movement of molecules against their concentration gradient is called ________.
A) active transport
B) diffusion
C) endocytosis
D) facilitated diffusion
E) osmosis
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytoplasm is found
A) in the nucleus.
B) outside the nucleus but inside the plasma membrane.
C) in the cisternae of the endoplasmic reticulum.
D) on the cristae of the mitochondria.
E) between the phospholipids in the plasma membrane.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following membrane proteins must be an integral protein to carry out its function?
A) Ion channel
B) Receptor protein
C) Enzyme
D) Marker molecule
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells that respond to ligands
A) possess receptor sites for specific ligands.
B) generally produce the ligands.
C) have lysosomes that destroy the ligands.
D) are using electrical signals in cellular communication.
E) are not functional.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs of terms is mismatched?
A) Mitochondria - cristae
B) Golgi apparatus - cisternae
C) Lysosomes - hydrolytic enzymes
D) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum - chromatin
E) Cilia - basal bodies
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which organelle packages materials for secretion from the cell?
A) Endoplasmic reticulum
B) Golgi apparatus
C) Nucleolus
D) Peroxisomes
E) Flagellum
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 230
Related Exams