A) C16H18N3ClS
B) Na2HPO3(H2O) 5
C) CH4
D) C3H7O2N
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical reactions with the property of being able to proceed from reactants to products and from products to reactants are called ________ reactions.
A) exchange
B) synthesis
C) decomposition
D) reversible
E) mirrored
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, their ions
A) cling tightly together.
B) dissociate or separate from one another.
C) lose their charge.
D) get lost in the solvent.
E) settle to the bottom of the container.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrogen bonds form between molecules containing ________ bonds; the hydrogen bond is between a hydrogen atom of one molecule and a partially ________ charged atom of another.
A) polar covalent; negatively
B) polar covalent; positively
C) nonpolar covalent; positively
D) nonpolar covalent; negatively
E) ionic; positively
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In ionic bonding,
A) only non-polar molecules are involved.
B) a "sea of electrons" forms.
C) electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
D) two hydrogen atoms share one pair of electrons.
E) the charge of the ion does not play a role in the bond.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 and an atomic mass of 16. How many valence electrons does it have?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 16
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ATP
A) is a nucleotide found in DNA.
B) stores genetic information.
C) is a sugar found in transfer RNA.
D) serves as the energy currency of the cell.
E) can store, but cannot release energy in the cell.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Normal blood pH is maintained within a range of
A) 7.35 - 8.5.
B) 7.35 - 7.45.
C) 4.5 - 5.5.
D) 1.0 - 14.0.
E) 6.5 - 9.5.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following subatomic particles can be changed in number without affecting the element identity of the atom?
A) Electrons
B) Protons
C) Neutrons
D) Both "electrons" and "neutrons" are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the first step of gene expression, an RNA copy of a gene is made. Which of the following represents the correct sequence produced from a gene segment with the following sequence: GAACTAAGC?
A) CUUGAUUCG
B) GAACUAAGC
C) CTTGATTCG
D) GUUCTUUGC
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a function of carbohydrates in the body?
A) Structural component of DNA
B) Protection
C) Bulk in feces
D) Energy
E) Structural component of RNA
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A base is a proton ________.
A) donor
B) converter
C) acceptor
D) creator
E) Both acceptor and creator are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Henry's science fair project focused on variation in the very obvious reaction between vinegar and baking soda. He noted that as he ________ the volume of vinegar, he saw a/an ________ in bubbling in the beaker.
A) increased; increase
B) decreased; decrease
C) increased; decrease
D) decreased; increase
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
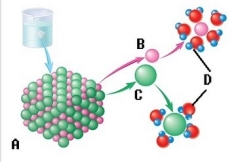 -The sodium chloride molecule breaks apart in water. What does "E" represent (the process) ?
-The sodium chloride molecule breaks apart in water. What does "E" represent (the process) ?
A) Chloride ion
B) Dissociation
C) Water molecule
D) Sodium ion
E) Salt crystal
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fatty acid A has 10 double covalent bonds scattered throughout its carbon chain while fatty acid B has only single covalent bonds between the carbons in its chain.
A) Fatty acid A is saturated.
B) Fatty acid B is unsaturated.
C) Both fatty acids are saturated.
D) Both fatty acids are unsaturated.
E) Fatty acid B is saturated.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An organic molecule such as a vitamin that makes an enzyme functional is called a/an ________.
A) buffer
B) coactivator
C) catalyst
D) coenzyme
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The smallest particle of an element that still exhibits the chemical characteristics of that element is a/an ________.
A) electron
B) atom
C) chemical bond
D) orbital
E) proton
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prions are pathogenic proteins that are linked to different neurodegenerative diseases. Investigations of some have indicated that normal cellular proteins and prions have the same amino acid sequence. How is this possible?
A) Though the primary structure is the same between the prion and the normal cellular protein, differences at higher levels (secondary or tertiary) alter protein activity.
B) The amino acid sequence is not important to the function of the protein because protein function is completely determined by the pH of the environment.
C) The double helix structure of proteins is easily altered by separating the nitrogenous bases holding the strands together, allowing for a protein to act as a prion.
D) The amino acids of the prion must have more hydrophilic sections, causing it to interact with the lipids of the plasma membrane and disrupting cell activity.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of matter in an object is its ________.
A) mass
B) weight
C) density
D) volume
E) size
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following nitrogen bases is found in RNA but not DNA?
A) Adenine
B) Guanine
C) Thymine
D) Uracil
E) Cytosine
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 207
Related Exams