A) discrimination.
B) differences in human capital.
C) differences in signaling.
D) chance.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nick and Daryn are both market analysts who started working for their current employer during the same year,graduated from the same university with bachelors' degrees in economics,and achieved similar performance reviews.Nick earned a master's degree last year.If Nick earns a higher annual salary than Daryn because he has more formal education,the employer is
A) paying a compensating differential.
B) paying efficiency wages.
C) practicing discrimination.
D) rewarding increases in human capital.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is systematic discrimination against a group of workers,then the wage paid to those workers likely will be
A) lower due to a higher supply of workers in that group.
B) lower due to a lower demand for workers in that group.
C) higher due to a lower supply of workers in that group.
D) higher due to a higher demand for workers in that group.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Between 1980 and 2008,the wage gap between women with a high school education and women with a college education has increased.In particular,in 2008 women with a college degree earned about
A) 12% more than women with a high school education.
B) 26% more than women with a high school education.
C) 42% more than women with a high school education.
D) 71% more than women with a high school education.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The fact that doctors are paid more than economics professors is an example of a compensating differential.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a compensating differential?
A) Two workers with different undergraduate majors earn different salaries.
B) Two workers with different years of experience earn different salaries.
C) Two workers whose jobs entail different working conditions earn different salaries.
D) Two workers with different levels of personal attractiveness earn different salaries.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If employers are profit-maximizers,then
A) competition will always eventually eliminate employment discrimination.
B) employment discrimination may persist if consumers discriminate.
C) employment discrimination will persist because it is always profitable.
D) compensating differentials cannot exist.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why would a wage differential due to discrimination be unlikely to persist in a competitive labor market?
A) There is a cost advantage for firms that do not discriminate.
B) Workers who are victims of discrimination will eventually drop out of the labor market.
C) Competing firms will hire fewer of the workers who are temporarily victimized by discrimination.
D) Discrimination cannot exist in markets.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Empirical work that does not account for differences in the productivity of workers
A) is unlikely to find evidence of wage differentials.
B) can provide strong evidence of labor market discrimination.
C) is likely to misinterpret apparent evidence of labor market discrimination.
D) is accepted as superior to empirical work that does correct for differences in productivity of workers.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A difference in wages between a highly-educated worker and a less-educated worker
A) may be due to a difference in the amounts of human capital between the workers..
B) may be a signal that the market is indifferent to a worker's level of human capital.
C) is considered unfair by economists.
D) is considered unfair by everyone.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Major league baseball players get paid more than minor league baseball players because of
A) compensating differentials.
B) higher levels of educational attainment.
C) greater abilities.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is increasingly clear that technological change is the only explanation for an expanding wage gap between high-skill and low-skill workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cory has just graduated from veterinary school.He can earn $40,000 working at a small animal clinic or $50,000 working with farm animals and horses where the risks of getting injured by an animal are higher.The higher salary to work with larger animals is an example of
A) a compensating differential.
B) signaling theory.
C) an efficiency wage.
D) efficient union bargaining.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 19-1 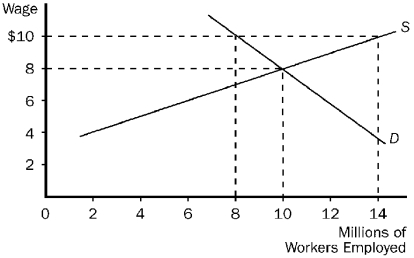 -Refer to Figure 19-1.Suppose the local labor market was in equilibrium to begin with but then the largest local employer decided to change its compensation scheme to $10 as shown.Which of the following compensation schemes could the graph be illustrating?
-Refer to Figure 19-1.Suppose the local labor market was in equilibrium to begin with but then the largest local employer decided to change its compensation scheme to $10 as shown.Which of the following compensation schemes could the graph be illustrating?
A) An efficiency wage.
B) Discrimination.
C) A compensating differential.
D) The superstar phenomenon.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements represents the idea behind signaling in education?
A) Education can turn an unproductive person into a productive person.
B) Education increases the marginal productivity of naturally productive workers.
C) The more naturally productive people are more inclined to educate themselves.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do major-league baseball players get paid more than minor-league players?
A) Major-league players are better athletes.
B) The higher wage reflects a compensating differential.
C) Playing in the major leagues in more pleasant then playing in the minor leagues.
D) The higher wage is often due to educational discrepancies.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not affect the wages a worker earns?
A) natural ability
B) effort
C) chance
D) All of the above affect the wages a worker earns.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If firms are competitive,then labor-market discrimination
A) cannot exist in either the short run or the long run.
B) will be more of a problem than if the market were monopolistic or imperfectly competitive.
C) likely will not be a long-run problem unless customers exhibit discriminatory preferences or government maintains discriminatory policies.
D) likely will be more of a problem in the long run than in the short run due to the zero-profit condition that characterizes long-run equilibrium for competitive firms.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 19-2 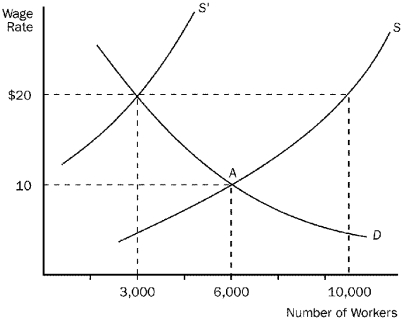 -Refer to Figure 19-2.This figure depicts labor demand and supply in a nonunionized labor market.The original equilibrium is at point A.If a labor union subsequently establishes a union shop and negotiates an hourly wage of $20,then the employment level
-Refer to Figure 19-2.This figure depicts labor demand and supply in a nonunionized labor market.The original equilibrium is at point A.If a labor union subsequently establishes a union shop and negotiates an hourly wage of $20,then the employment level
A) increases from 6,000 to 10,000.
B) increases from 3,000 to 10,000.
C) decreases from 10,000 to 3,000.
D) decreases from 6,000 to 3,000.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fact that movie star Julia Roberts's salary is much higher than the salary earned by the world's best plumber can best be explained by the
A) failure of the market to reward talent fairly.
B) fact that wage rates cannot reflect the influence of education properly.
C) willingness of some people to accept a lower wage rate in order to do what they like most to do.
D) superstar phenomenon.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 425
Related Exams