B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A modern system of classification gives the category name domain to
A) insects.
B) Prokaryota.
C) Hominidae.
D) Fungi.
E) Eukarya.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Two butterflies have identical wing patterns, but in one the pigment is blue and in the other the pigment is yellow. The original ancestor had green wing pigments. The wing pigment is an example of a(n) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Explain how systematics and Linnaean taxonomy differ.
Correct Answer

verified
Linnaean taxonomy is based on ...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the smallest or least inclusive group?
A) Kingdom
B) Species
C) Genus
D) Class
E) Order
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The science of reconstructing an organism's evolutionary history is called systematics.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which biologist first proposed that all organisms share a common ancestry?
A) Aristotle
B) Linnaeus
C) Whittaker
D) Woese
E) Darwin
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
How did Darwin's evolutionary theory change the significance of the taxonomic categories of organisms?
Correct Answer

verified
Taxonomic categories...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the smallest or least inclusive group?
A) Genus
B) Kingdom
C) Family
D) Domain
E) Class
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who was the Swedish naturalist who established the modern system for classifying organisms?
A) Aristotle
B) Linnaeus
C) Whittaker
D) Woese
E) Darwin
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Scientists currently identify three domains: plants, animals, and bacteria.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The smallest diagnosable group that contains all the descendants of a single common ancestor is a(n) .
Correct Answer

verified
phylogenet...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
Sponges and worms belong to the domain .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Based on the eukaryotic tree, gymnosperms are most closely related to
-Based on the eukaryotic tree, gymnosperms are most closely related to
A) chlorophyta.
B) oomycota.
C) porifera.
D) angiosperms.
E) zygomycota.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA analysis reveals that two species of birds appear to have evolved from a common ancestor. These two species belong to the same
A) gene pool.
B) species.
C) breeding group.
D) clade.
E) nest group.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which group contains mostly unicellular, eukaryotic organisms?
A) Bacteria
B) Animalia
C) Protists
D) Plantae
E) Fungi
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Once an organism is placed in a specific species, the designation cannot be changed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparing the chromosomes of chimpanzees and humans has revealed that the two species
A) are only distantly related.
B) should be classified in the same species.
C) should be classified in the same genus.
D) are closely related.
E) should not be classified in the same family.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
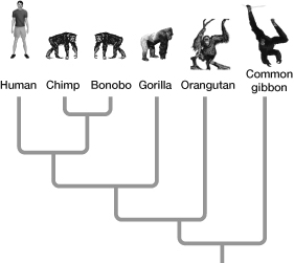
Multiple Choice
 -Based on the evolutionary tree shown here, which two organisms are most closely related?
-Based on the evolutionary tree shown here, which two organisms are most closely related?
A) Humans and orangutans
B) Chimps and bonobos
C) Orangutans and common gibbons
D) Humans and gorillas
E) Common gibbons and chimps
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genetics studies of human populations have revealed that
A) it is nearly impossible to determine the relatedness of human populations.
B) Homo sapiens probably did not evolve from primates.
C) all humans are virtually identical.
D) humans have very little genetic variation compared to other mammals.
E) human populations vary tremendously at the level of DNA sequences.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 90
Related Exams