A) information is retained for less than a second.
B) the frontal lobe plays the most important role.
C) current information is lost when new information is presented.
D) there is increased synaptic activity by long-term potentiation.
E) there is consolidation of information.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
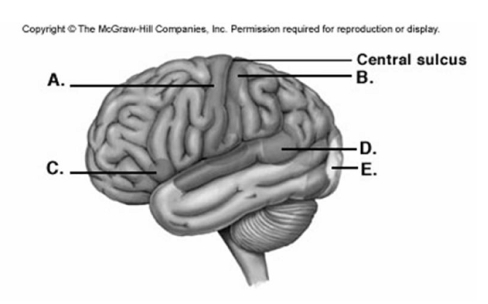 -Label area "E" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "E" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca'sarea)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) left cerebral hemisphere - analytical hemisphere
B) left cerebral hemisphere - speech area for most of the population
C) right cerebral hemisphere - recognition of faces
D) left cerebral hemisphere - spatial perception
E) left cerebral hemisphere - mathematical hemisphere
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient has suffered a cerebral hemorrhage that has damaged the primary motor area of his right cerebral cortex. As a result the
A) patient cannot voluntarily move his right arm or leg.
B) patient feels no sensations on the left side of his body.
C) patient cannot voluntarily move his left eye.
D) patient's heart stops beating.
E) patient cannot voluntarily move his left arm or leg.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The simplest and most common type of sensory nerve endings are free nerve endings.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Visual input is sent to the brainstem via the _____ nerve, whereas the _____ nerve sends facial sensation to the brainstem.
A) trigeminal; accessory
B) facial; trochlear
C) optic; facial
D) optic; trigeminal
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of adaptation of receptors would be _____.
A) being aware of our body parts at all times
B) continual monitoring touch signals
C) ignoring the presence of clothes
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nurse is caring for a patient who exhibits the following symptoms: (1) inability to maintain balance while walking (2) normal intelligence (3) can initiate voluntary movements although they are somewhat uncoordinated. (4) decreased tone in the skeletal muscles The patient is probably suffering from a condition that affected the
A) midbrain.
B) cerebellum.
C) basal ganglia.
D) cerebral cortex.
E) brainstem.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Label area "C" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "C" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -hippocampus
A) the part of the brain involved in the actual declarative memory
B) the largest of the cerebral commissures
C) a factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) a series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) a part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
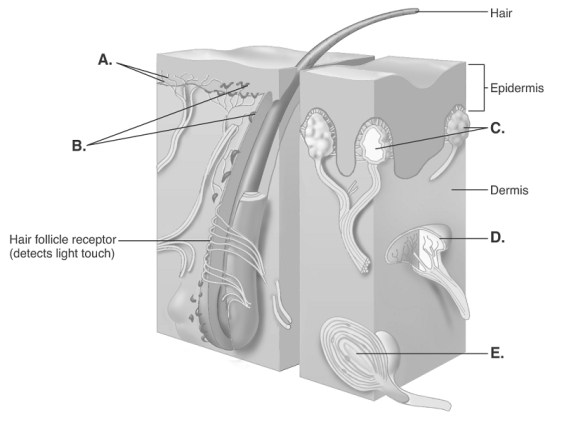 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "D" represent?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "D" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) Merkel disks - light touch
B) Pacinian corpuscles - vibration
C) Meissner corpuscles - two-point discrimination
D) Ruffini end organs - temperature
E) hair follicle receptors - slight bending of the hair
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary motor area
A) contains sensory neurons for the face in its inferior portion.
B) contains a smaller area for control of the hands than for control of the legs.
C) contains neurons that control smooth muscle.
D) contains more motor neurons for the thighs than the mouth.
E) contains a larger area for control of the hand and fingers than for control of the arm and elbow.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Label area "B" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "B" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The EEG of a normal person exhibits mostly irregular patterns.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a person is exposed to temperature extremes, why is it difficult to distinguish hot from cold objects?
A) Temperature perception requires more than one type of receptor.
B) Temperatures above 37 degrees centigrade actually stimulate the cold receptors.
C) At extremes, pain receptors are stimulated by both very hot and very cold objects.
D) Most temperature receptors cannot differentiate hot from cold.
E) Pain receptors are inhibited by both very hot and very cold objects.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Various areas of the cortex form functional pathways to conduct action potentials necessary to perform specific functions. Arrange the areas below in proper sequence to accomplish reading a poem aloud. (1) visual association area (2) premotor area (3) Broca area (4) primary motor area (5) Wernicke area (6) visual cortex
A) 1, 6, 5, 3, 4, 2
B) 6, 1, 5, 3, 2, 4
C) 6, 1, 3, 5, 4, 2
D) 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 3
E) 5, 4, 3, 6, 1, 2
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -amygdala
A) the part of the brain involved in the actual declarative memory
B) the largest of the cerebral commissures
C) a factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) a series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) a part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ability to localize the position of body parts is called
A) two-point discrimination.
B) proprioception.
C) fine touch.
D) light touch.
E) perception.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The taste area is located in the
A) insula.
B) parietal lobe.
C) frontal lobe.
D) temporal lobe.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 142
Related Exams