A) temporal lobe
B) cerebellum
C) frontal lobe
D) occipital lobe
E) parietal lobe
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small lesion in the brainstem which resulted in a rapid heart rate, intense vasoconstriction, and elevated blood pressure would probably be located in the
A) medulla oblongata.
B) pons.
C) cerebellum.
D) hypothalamus.
E) cerebrum.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From which embryonic brain region does the medulla oblongata form?
A) telencephalon
B) diencephalon
C) mesencephalon
D) metencephalon
E) myelencephalon
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Roman numerals assigned to each cranial nerve reflect
A) the order of their discovery.
B) the sequence from anterior to posterior in which they emerge from the brain.
C) their importance, with highest numbers being the most important.
D) the complexity of each nerve, with complex nerves having higher numbers.
E) the sequence from posterior to anterior in which they emerge from the brain.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cerebrum develops from the embryonic region called the
A) telencephalon.
B) mesencephalon.
C) diencephalon.
D) metencephalon.
E) rhombencephalon.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the function with the correct lobe of the brain. -insula
A) important in voluntary motor function
B) fifth lobe of the brain
C) plays an important role in memory
D) reception and integration of visual input
E) reception of most sensory input
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the ____ and is reabsorbed by the ____.
A) choroid plexus, arachnoid granulation
B) arachnoid granulation, choroid plexus
C) dural sinus, dura mater
D) dura mater, dural sinus
E) septa pellucida, cerebral aqueduct
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
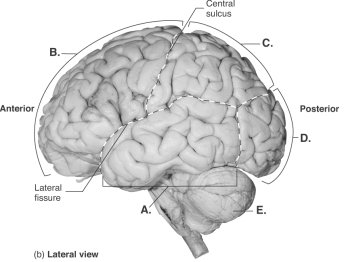 -This is a lateral view of the brain. What does "E" represent?
-This is a lateral view of the brain. What does "E" represent?
A) temporal lobe
B) cerebellum
C) frontal lobe
D) occipital lobe
E) parietal lobe
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cerebral medulla
A) has the same function as the medulla oblongata.
B) is the gray matter on the cerebrum's surface.
C) consists of many nerve tracts of white matter beneath the cerebral cortex.
D) is another name for the basal nuclei.
E) is the outer layer of the cerebrum.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fibers connecting areas of the cerebral cortex within the same hemisphere are ______ fibers.
A) commissural
B) projection
C) association
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
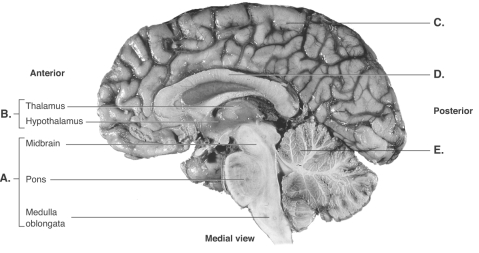 -This is a midsagittal section of the right half of the brain. What does "D" represent?
-This is a midsagittal section of the right half of the brain. What does "D" represent?
A) cerebrum
B) cerebellum
C) corpus callosum
D) diencephalon
E) brainstem
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning the brainstem is true?
A) The brainstem consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum.
B) The brainstem is responsible for higher level thinking skills.
C) Damage to the brainstem is usually fatal.
D) All twelve cranial nerves enter or exit from the brainstem.
E) The brainstem is a relay for sensory input.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would help to determine if the oculomotor nerve was damaged?
A) have the patient distinguish between green and red colors
B) determine if the patient can see anything
C) have the patient look superiorly and inferiorly
D) have the patient cry
E) determine if the patient still has night vision
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Paralysis on the right side of the face could result from damage to the right _____ nerve.
A) vagus
B) facial
C) accessory
D) trigeminal
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The facial and glossopharyngeal nerves
A) innervate the salivary glands.
B) control movements of the tongue.
C) are involved in the sense of smell.
D) control the production of tears.
E) carry pain from the teeth.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pyramids of the medulla contain
A) ascending motor tracts.
B) descending motor tracts.
C) ascending sensory tracts.
D) descending sensory tracts.
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Thirteen year-old Austin exhibits retarded growth, reduced metabolism, lack of normal reproductive gland development, inability to regulate water intake or water elimination from the body, and an uncontrolled appetite. What part of Austin's brain is most likely involved?
A) reticular formation
B) primary sensory cortex
C) medulla oblongata
D) thalamus
E) hypothalamus
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pineal body
A) connects the two cerebral hemispheres.
B) modifies mood.
C) causes hot and cold flashes.
D) appears to play a role in controlling the onset of puberty.
E) plays a role in the production of cerebrospinal fluid.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which area of the brain contains areas that initiates REM sleep?
A) medulla oblongata
B) pons
C) thalamus
D) midbrain
E) diencephalon
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
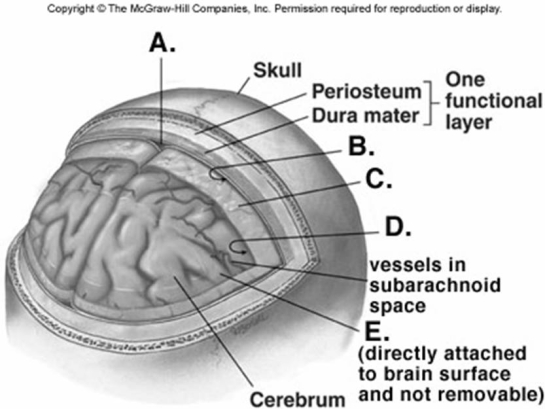 -What does "C" represent on the diagram of the skull and brain?
-What does "C" represent on the diagram of the skull and brain?
A) subarachnoid space
B) dural venous sinus
C) pia mater
D) arachnoid mater
E) subdural space
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 158
Related Exams