A) inhibition of acetylcholine molecules.
B) blockage of acetylcholine receptors.
C) inhibition of acetylcholinesterase.
D) destruction of synaptic vesicles.
E) increase in the amount of acetylcholinesterase.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The length of the resting sarcomere is
A) longer than the length of a contracted sarcomere.
B) shorter than the length of a contracted sarcomere.
C) the same length as a contracted sarcomere.
D) the same length as the muscle fiber.
E) the same length as the myofibril.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning smooth muscle is true?
A) It contains many sarcomeres.
B) Caveolae seem to take the place of the myofibrils.
C) A calcium-calmodulin complex initiates cross-bridge formation.
D) The cells are large and multinuclear.
E) It has a well developed sarcoplasmic reticulum.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increased strength of a trained muscle is due to
A) an increased number of muscle fibers.
B) the nervous system's ability to recruit a large number of motor units simultaneously.
C) elimination of unnecessary enzymes and metabolic pathways.
D) elimination of all fat deposits.
E) elimination of unnecessary connective tissue.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The capacity of a muscle cell to shorten forcefully is known as
A) contractility.
B) excitability.
C) extensibility.
D) elasticity.
E) flexibility.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
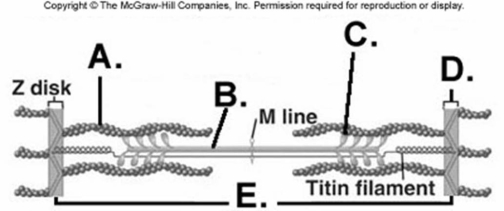 -What does "D" represent on the diagram?
-What does "D" represent on the diagram?
A) myosin myofilament
B) actin myofilament
C) sarcomere
D) Z disk
E) cross-bridge
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sites where a chemical substance is transmitted from the presynaptic terminal of an axon to the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber are called
A) neuromuscular junctions.
B) sarcomeres.
C) myofilaments.
D) Z disks.
E) cell body of neuron.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sarcolemma is the
A) cell membrane of a muscle fiber.
B) cytoplasm of muscle cells.
C) structural and functional unit of the skeletal muscle cell.
D) contractile thread that extends the length of the muscle fiber.
E) protein strand composed of actin.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly describes myoglobin's special function in muscle tissue?
A) breaks down glycogen
B) synthesizes ATP
C) acts as a reservoir for oxygen
D) produces action potentials
E) stores glucose
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Physiological contracture
A) occurs when muscles are resting.
B) is a condition in which cross-bridges cannot release.
C) is caused by an abundance of ATP in muscle fibers.
D) results when muscles are well exercised.
E) results when the neurotransmitter remains in the receptor.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In excitation-contraction coupling,
A) calcium ions must bind with myosin to expose active sites on actin.
B) myosin heads bind to exposed active sites on actin.
C) cross-bridges form between myosin heads and calcium ions.
D) movement of the troponin-tropomyosin complex causes actin myofilaments to slide.
E) ATP binds to actin myofilaments.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following connective tissue layers is outside all the others?
A) perimysium
B) endomysium
C) epimysium
D) paramysium
E) sarcolemma
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lack of acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft would result in
A) a decrease in acetylcholine production by the motor neuron.
B) continuous stimulation of the postsynaptic membrane.
C) rapid degradation of acetylcholine.
D) relaxation of the muscle.
E) continuous stimulation of the presynaptic membrane.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
List the following structures in order from smallest to largest. (1) muscle fiber (2) myofilament (3) myofibril (4) muscle fasciculus
A) 4, 2, 3, 1
B) 2, 1, 4, 3
C) 3, 1, 4, 2
D) 2, 3, 1, 4
E) 1, 2, 3, 4
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a contracted muscle, the A bands do narrow because the length of the myosin myofilaments changes,.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The condition of painful, spasmodic contractions of muscles is referred to as
A) cramps.
B) fibrositis.
C) fibromyalgia.
D) muscular dystrophy.
E) paralysis.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the statement concerning skeletal muscle that is true.
A) It comprises about 20% of the body's weight.
B) It propels urine through the urinary tract.
C) Its function is largely under involuntary control.
D) It is a kind of connective tissue.
E) It is responsible for locomotion.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A lack of mitochondria within skeletal muscle would impair which ATP-yielding chemical process?
A) anaerobic respiration
B) aerobic respiration
C) both anaerobic and aerobic respiration
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Depolarization of the cell membrane occurs when there is a rapid influx (inflow) of
A) potassium ions.
B) chloride ions.
C) calcium ions.
D) sodium ions.
E) amino acids.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tetanus of a muscle is thought to be caused by
A) high calcium ion concentrations in the sarcoplasm.
B) the rapid movement of sodium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) an increase in stimulus strength.
D) increased temperature in the active muscle.
E) decreased amounts of calcium ions in muscle tissue.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 200
Related Exams