A) inhibit the enzyme and thus slow the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
B) activate the enzyme and thus slow the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
C) inhibit the enzyme and thus increase the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
D) activate the enzyme and increase the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
E) inhibit the enzyme and thus increase the rate of glycolysis and the concentration of citrate.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphofructokinase is an important control enzyme in the regulation of cellular respiration. Which of the following statements correctly describes phosphofructokinase activity?
A) It is inhibited by AMP.
B) It is activated by ATP.
C) It is activated by citrate, an intermediate of the citric acid cycle.
D) It catalyzes the conversion of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate, an early step of glycolysis.
E) It is an allosteric enzyme.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the molecule becomes
A) hydrolyzed.
B) hydrogenated.
C) oxidized.
D) reduced.
E) an oxidizing agent.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What fraction of the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals is generated by the reactions of the citric acid cycle, if glucose is the sole energy source?
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 1/2
D) 2/3
E) 100/100
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is glycolysis described as having an investment phase and a payoff phase?
A) It both splits molecules and assembles molecules.
B) It attaches and detaches phosphate groups.
C) It uses glucose and generates pyruvate.
D) It shifts molecules from cytosol to mitochondrion.
E) It uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are carbohydrates and fats considered high-energy foods?
A) They have a lot of oxygen atoms.
B) They have no nitrogen in their makeup.
C) They can have very long carbon skeletons.
D) They have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
E) They are easily reduced.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, using the energy released by movement of protons across the membrane down their electrochemical gradient, is an example of
A) active transport.
B) an endergonic reaction coupled to an exergonic reaction.
C) a reaction with a positive ΔG.
D) osmosis.
E) allosteric regulation.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of mitochondria, which of the following changes occurs?
A) The pH of the matrix increases.
B) ATP synthase pumps protons by active transport.
C) The electrons gain free energy.
D) The cytochromes phosphorylate ADP to form ATP.
E) NAD⁺ is oxidized.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where is ATP synthase located in the mitochondrion?
A) cytosol
B) electron transport chain
C) outer membrane
D) inner membrane
E) mitochondrial matrix
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule?
A) the citric acid cycle
B) the electron transport chain
C) glycolysis
D) synthesis of acetyl CoA from pyruvate
E) reduction of pyruvate to lactate
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions.
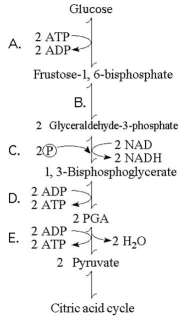 -Which step in the figure above is a redox reaction?
-Which step in the figure above is a redox reaction?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is
A) oxygen.
B) water.
C) NAD⁺.
D) pyruvate.
E) ADP.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When skeletal muscle cells are oxygen-deprived, the heart still pumps. What must the heart muscle cells be able to do?
A) derive sufficient energy from fermentation
B) continue aerobic metabolism when skeletal muscle cannot
C) transform lactate to pyruvate again
D) remove lactate from the blood
E) remove oxygen from lactate
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules?
A) anabolic pathways
B) catabolic pathways
C) fermentation pathways
D) thermodynamic pathways
E) bioenergetic pathways
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and water is -686 kcal/mol and the free energy for the reduction of NAD⁺ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed?
A) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
B) Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
C) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
D) There is no CO₂ or water produced as products of glycolysis.
E) Glycolysis consists of many enzymatic reactions, each of which extracts some energy from the glucose molecule.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis?
A) CO₂ and H₂O
B) CO₂ and pyruvate
C) NADH and pyruvate
D) CO₂ and NADH
E) H₂O, FADH₂, and citrate
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, the result is the
A) formation of ATP.
B) reduction of NAD⁺.
C) restoration of the Na⁺/K⁺ balance across the membrane.
D) creation of a proton-motive force.
E) lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During respiration, energy flows in the following sequence.
A) glucose → NADH → electron transport → oxygen
B) glucose → electron transport → NADH → proton-motive force → ATP
C) pyruvate → acetyl-CoA → electron transport → water
D) glucose → pyruvate → acetyl-CoA → CO₂
E) glucose → NADH → electron transport → proton-motive force → ATP
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the purpose of beta oxidation in respiration?
A) oxidation of glucose
B) oxidation of pyruvate
C) feedback regulation
D) control of ATP accumulation
E) breakdown of fatty acids
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During intense exercise, as skeletal muscle cells go into anaerobiosis, the human body will increase its catabolism of
A) fats only.
B) carbohydrates only.
C) proteins only.
D) fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
E) fats and proteins only.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 117
Related Exams