B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A typical American worker covered by unemployment insurance receives
A) 50 percent of his former wages for 26 weeks.
B) 50 percent of his former wages for 52 weeks.
C) 100 percent of his former wages for 26 weeks.
D) 100 percent of his former wages for 52 weeks.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cyclical unemployment is closely associated with
A) long-term economic growth.
B) short-run ups and downs of the economy.
C) fluctuations in the natural rate of unemployment.
D) changes in the minimum wage.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not help reduce frictional unemployment?
A) government-run employment agencies
B) public training programs
C) unemployment insurance
D) All of the above help reduce frictional unemployment.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28-1  -Refer to Figure 28-1.If the government imposes a minimum wage of $8,then employment will decrease by
-Refer to Figure 28-1.If the government imposes a minimum wage of $8,then employment will decrease by
A) 0 workers.
B) 2000 workers.
C) 3000 workers.
D) 4000 workers.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Structural unemployment results when the number of jobs is insufficient for the number of workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Within the U.S.population,teenagers have similar rates of labor-force participation as older workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who is included in the labor force by the Bureau of Labor Statistics?
A) Aibne,who works most of the week in a steel factory
B) Modlen,who is waiting for her new job at the bank to start
C) Wyclef,who does not have a job,but is looking for work
D) All of the above are included in the labor force.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most people rely on income other than their labor earnings to maintain their standard of living.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics produces data on unemployment,types of employment,length of the average workweek,and the duration of unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a minimum-wage law forces the wage to remain above the level that balances supply and demand,it
A) raises the quantity of labor supplied and raises the quantity of labor demanded compared to the equilibrium level.
B) raises the quantity of labor supplied and reduces the quantity of labor demanded compared to the equilibrium level.
C) reduces the quantity of labor supplied and raises the quantity of labor demanded compared to the equilibrium level.
D) reduces the quantity of labor supplied and reduces the quantity of labor demanded compared to the equilibrium level.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) Most people who become unemployed will soon find jobs.
B) In an ideal labor market,wages would adjust to ensure that all workers are always fully employed.
C) The unemployment rate occasionally falls to zero.
D) There are always some workers without jobs,even when the overall economy is doing well.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Public policy
A) can reduce both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
B) can reduce frictional unemployment,but it cannot reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
C) cannot reduce frictional unemployment,but it can reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
D) cannot reduce either frictional unemployment or the natural rate of unemployment.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Over the past several decades,the difference between the labor-force participation rates of men and women in the U.S.has gradually increased.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Over the past several decades in the United States,the labor-force participation rate of women has increased and the labor-force participation rate of men had remained steady.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who is not included in the labor force by the Bureau of Labor Statistics?
A) Kawanari,who is on temporary layoff
B) Takuji,who has retired and is not looking for work
C) Izumi,who does not have a job,but has applied for several in the last week
D) None of the above is correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Table 28-5
2010 Labor Data for Wrexington
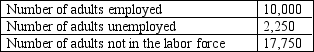 -Refer to Table 28-5.The labor-force participation rate of Wrexington in 2010 is about 40.8 percent.
-Refer to Table 28-5.The labor-force participation rate of Wrexington in 2010 is about 40.8 percent.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Data on the unemployment rate in the U.S.since 1960 show that the economy
A) always has some unemployment and that the amount stays constant from year to year.
B) always has some unemployment and that the amount changes from year to year.
C) sometimes has some unemployment and that the amount stays constant from year to year.
D) sometimes has some unemployment and that the amount changes from year to year.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics defines marginally attached workers as persons who currently are neither working nor looking for work but indicate that they want and are available for a job and have looked for work sometime in the recent past.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
More than one-third of the unemployed are recent entrants into the labor force.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 321 - 340 of 533
Related Exams