A) Penetration pricing is a profit-oriented approach to pricing.
B) Penetration pricing is a cost-oriented pricing method.
C) Penetration pricing encourages competitors to enter a market.
D) Penetration pricing is more effective in a marketplace with price-sensitive consumers.
E) Penetration pricing usually precedes a skimming pricing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bob Biltmore owns dozens of successful print shops in the Midwest.Biltmore's shops specialize in low-cost,black-and-white copies and feature user-friendly machines consumers can easily operate.In recent months,Biltmore has noticed more competition near his stores.In an attempt to eliminate the competition,Biltmore has decided to charge a very low price for his black-and-white copies,a price so low his competitors will be forced to close.After that,Biltmore plans to raise copy prices.He plans to engage in the illegal and unethical practice of
A) price fixing.
B) price inflation.
C) deceptive pricing.
D) competitive pricing.
E) predatory pricing.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Creative marketers engage in value-pricing,which is the practice of simultaneously __________ while maintaining or decreasing price.
A) promoting specific product and service benefits
B) increasing product and service benefits
C) decreasing profit
D) analyzing benefits
E) decreasing cost
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-2 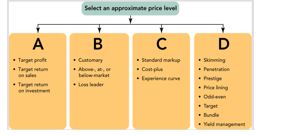 -Figure 11-2 represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level.Box B includes standard markup and cost-plus so it represents which approach?
-Figure 11-2 represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level.Box B includes standard markup and cost-plus so it represents which approach?
A) demand-oriented approach
B) profit-oriented approach
C) competition-oriented approach
D) results-oriented approach
E) cost-oriented approach
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bundle pricing is considered to be a __________ pricing practice.
A) demand-oriented
B) cost-oriented
C) profit-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) product line-oriented
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of discount to resellers is based in part on where they are in the channel?
A) seasonal discounts
B) trade discounts
C) cash discounts
D) promotional allowances
E) trade-in allowances
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate a firm's profit using the following information: the unit price (P) for a product is $40; the quantity sold (Q) is 2,000; the fixed cost (FC) is $50,000; and the variable cost (VC) is $20 ,000.
A) $10,000
B) $50,000
C) $110,000
D) $150,000
E) cannot be determined with the information provided
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Amazon wanted lower retail prices for e-books to
A) lower royalties to authors.
B) eliminate distributors.
C) raise prices overall for printed books.
D) undermine its rival, Barnes & Noble.
E) build its e-book business.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A manufacturer of a portable digital HD camera is considering a skimming pricing strategy for its new product.Which of the following conditions would argue against using a skimming pricing strategy for the camera?
A) There will be a large potential market, even if the product is sold at a high price.
B) Technological problems still exist for competitors; their products are not equivalent.
C) Increasing the volume sold reduces production costs substantially.
D) Consumers perceive a strong price-quality relationship for this product.
E) Many consumers in the target market are innovators.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sum of the expenses of a firm that is stable and does not change with the quantity of the product that is produced and sold is referred to as
A) fixed cost.
B) total cost.
C) variable cost.
D) marginal cost.
E) overhead cost.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yield management pricing is most consistent with services trying to deal with
A) perceived risk.
B) capacity management.
C) cognitive dissonance.
D) inelasticity of demand.
E) new product strategy development.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yield management pricing refers to
A) controlling the production of products based upon seasonal demand.
B) deliberately selling a product below its customary price, not to increase sales, but to attract customers' attention in hopes that they will buy other products as well.
C) charging the same prices during different times of the day or days of the week to reflect variations in supply for the service.
D) offering significant price discounts to wholesalers that agree to purchase products in advance for a period of a year or more at a time.
E) charging different prices to maximize revenue for a set amount of capacity at any given time.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marketers using a dynamic price policy should take care to avoid
A) requests for allowances.
B) price discrimination.
C) contradictory promotions.
D) changes in market segmentation.
E) support from government agencies.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Variable cost refers to
A) the sum of the expenses of the firm that are stable and do not change with the quantity of a product that is produced and sold.
B) the sum of the expenses of the firm that change with the quantity of a product that is produced and sold.
C) the total expense incurred by a firm in producing and marketing a product, which equals the sum of fixed cost and marginal cost.
D) the average amount of money received for selling one unit of a product or simply the price of that unit.
E) the change in total cost that results from producing and marketing one additional unit of a product.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following statements about standard markup pricing are true except which?
A) High-volume products usually have smaller markups than do low-volume products.
B) The percentage markup depends on the type of retail store and the product involved.
C) Markups must cover all expenses of the store, pay for overhead costs, and contribute something to profits.
D) The method involves summing the total unit cost of providing a product or service and adding a specific amount to the cost to arrive at a price.
E) Supermarket managers use this method since they have such a large number of products that estimating the demand for each product as a means of setting price is impossible.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantity at which total revenue and total cost are equal is referred to as
A) the tipping point.
B) the profitability point.
C) incremental return on investment.
D) the break-even point.
E) sustainability.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What pricing method is often used because of the difficulty in establishing a benchmark of sales or investment to show how much of a firm's effort is needed to achieve the target?
A) target return-on-investment pricing
B) target return-on-sales pricing
C) standard markup pricing
D) target pricing
E) loss-leader pricing
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skimming pricing is considered to be a __________ approach to pricing.
A) demand-oriented
B) cost-oriented
C) profit-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deceptive pricing practices are outlawed by legislation and enforced by which federal agency?
A) Consumer Protection Agency
B) U.S. Department of Justice
C) Federal Communications Commission
D) U.S. Department of Commerce
E) Federal Trade Commission
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Seasonal discounts are used by manufacturers to
A) get rid of dated merchandise.
B) prevent retailers from purchasing competitors' products.
C) prolong the peak seasonal selling season.
D) establish an immediate feeling of goodwill between the buyer and seller that hopefully will continue when prices return to normal.
E) entice dealers to purchase seasonal merchandise earlier in the selling season.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 374
Related Exams