A) the strategy used by multinational firms that have as many different product variations, brand names, and advertising programs as countries in which they do business.
B) the strategy of transnational firms not to employ adaptive marketing techniques when there are cultural differences, but to redirect their marketing resources towards customer education.
C) the strategy of transnational firms that employ the practice of standardizing marketing activities when there are cultural similarities and adapting them when cultures differ.
D) the global strategy of seeking out already established firms in other nations and selling them the rights to manufacture and distribute the firm's products through a host nation's local businesses.
E) the strategy currently used by most U.S. domestic firms that when entering a new international market, these firms offer only those products that require the least amount of product adaptation.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Five trends in the past decade have significantly influenced the landscape of global marketing. One of them is
A) an increase in economic protectionism and a decline in free trade.
B) a more aggressive attitude towards initiating international tariffs and quota systems.
C) global competition among global companies for global customers.
D) a decrease in most countries' GDPs and a renewal of nationalism.
E) an increase in most countries' GDPs coupled with an increased degree of consumer ethnocentrism.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Beginning January 1, 2005, China lifted the import quotas and lowered tariffs on automobiles. This removal of the quotas and the lowering of tariffs is an example of
A) relaxing the rule of eminent domain.
B) reducing ethnocentrism.
C) enhancing domestic imperialism.
D) reducing protectionism.
E) enhancing countertrade
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A gray market refers to
A) the segment of products specifically designed for the need of older buyers.
B) a once active and powerful market that is rapidly becoming the bottom of the barrel.
C) a situation where products are sold through unauthorized channels of distribution.
D) a pricing structure that is based upon haggling that is considered acceptable in some countries but not others.
E) the willingness of one party to accept gifts in exchange for better prices or price allowances.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The argument for protectionism is that it
A) protects a nation's political security.
B) encourages economic reliance on foreign countries.
C) inhibits the development of domestic industries.
D) creates opportunities for the outsourcing of domestic jobs.
E) creates a more favorable environment for a global economy.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of the global marketplace, there are three primary types of companies: international firms, __________ firms, and transnational firms.
A) large-scale
B) conglomerate
C) intercontinental
D) cosmopolitan
E) multinational
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
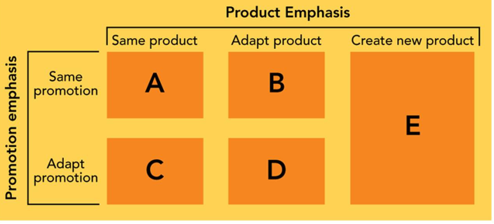 -Global companies have five strategies for matching products and their promotion efforts to global markets. According to Figure 6-4 above, B refers to which type of strategy?
-Global companies have five strategies for matching products and their promotion efforts to global markets. According to Figure 6-4 above, B refers to which type of strategy?
A) product extension strategy
B) communication adaptation strategy
C) product adaptation strategy
D) dual adaptation strategy
E) product invention strategy
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Disney employed a(n) __________ marketing strategy for its Disneyland Paris, particularly when it came to the eateries in the park. These restaurants featured recipes that were revised for local tastes, alcoholic beverages (not permitted in previous parks) , and increased outdoor seating.
A) global
B) transnational
C) multidomestic
D) meganational
E) international
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
KFC in Japan sells tempura crispy strips. In northern England, it stresses gravy and potatoes. In Thailand, it offers fresh rice. In Holland, instead of potatoes, KFC offers customers a potato and onion croquette. In France, KFC sells pastries alongside its chicken. These examples illustrate that KFC exhibits an appreciation for the __________ of other societies.
A) demographics
B) symbols
C) sensitivities
D) customs
E) values
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are __________ World Trade Organization countries, including the United States, which account for more than 90 percent of world trade.
A) 37
B) 52
C) 97
D) 113
E) 159
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The practice of shielding one or more sectors of a country's economy from foreign competition through the use of tariffs or quotas is referred to as
A) domestic imperialism.
B) protectionism.
C) blocked competition.
D) import taxation.
E) trade restriction.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What global market-entry strategy involves slightly more risk than indirect exporting for a company but also opens the door to increased profits?
A) direct exporting
B) licensing
C) cooperative
D) joint venture
E) direct investment
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning currency exchange rates is most accurate?
A) Fluctuations in exchange rates among the world's currencies are of critical importance in global marketing.
B) Fluctuations in exchange rates among the world's currencies occur, but multinational companies are insulated from the affects because of direct investment.
C) Exchange rate fluctuations are relatively rare, but when they occur, their effects are minimal.
D) Exchange rate fluctuations are now almost nonexistent due in great part to the stability of the euro.
E) Exchange rate fluctuations may affect the financial sector but rarely reach the consumer.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To eliminate the need to continually monitor currency exchange rates, __________ of the countries in the European Union (EU) have adopted a common currency called the euro.
A) 11
B) 16
C) 20
D) 28
E) 32
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is considered normal and expected about the way people do things in a specific country is referred to as __________.
A) morals
B) ethics
C) values
D) customs
E) beliefs
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which form of entry into a foreign market requires the greatest commitment?
A) direct exporting
B) direct investment
C) joint venture
D) licensing
E) indirect exporting
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Latvia, only one six-lane highway exists, connecting Riga, its capitol, with Moscow. Otherwise, the roads are two-lane and many are made of cobblestones or bricks. This limits the speed with which deliveries can be made and requires that delivery trucks be quite small. The road network in Latvia is an example of problems with a country's
A) capital improvements.
B) fixed-asset base.
C) geopolitical wealth.
D) asset wealth.
E) economic infrastructure
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generally speaking, a(n) __________ firm markets its existing products and services in other countries the same way it does in its home country.
A) meganational
B) international
C) multinational
D) transnational
E) intranational
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Indirect exporting refers to
A) offering the right to a trademark, patent, trade secret, or similarly valued item of intellectual property in return for a royalty or fee.
B) selling a firm's domestically produced products in a foreign country without interference by that government.
C) contracting with a foreign firm to manufacture products according to stated specifications.
D) avoiding the use of additional parties when a firm sells its domestically produced products in another country.
E) selling a firm's domestically produced products in a foreign country through an intermediary.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding global brands is most accurate?
A) A global brand has dispersed marketing centers, each of which is responsible for a specific region.
B) A global brand is marketed under the same name in multiple countries.
C) A global brand alters the brand name for each dialect in a geographical region.
D) A global brand delivers multiple benefits to the GDP of each country.
E) A global brand is a collaborative effort among several different transnational firms.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 239
Related Exams