A) why most demand curves slope downward.
B) the tradeoff between work and leisure
C) how interest rates affect household saving.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The income effect of a price change is the change in consumption that results from the movement to a new indifference curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The direction of the substitution effect is not influenced by whether the good is normal or inferior.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A budget constraint illustrates bundles that a consumer prefers equally,while an indifference curve illustrates bundles that are equally affordable to a consumer.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following equations corresponds to an optimal choice point? (i) MRS = PX/PY (ii) MUX/MUY = PX/PY (iii) MUX/PX = MUY/PY (iv) MUX/PY = MUY/PX
A) (i) only
B) (i) ,(ii) ,and (iii) only
C) (ii) and (iv) only
D) (i) ,(ii) ,(iii) ,and (iv)
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Caroline is indifferent between tea and coffee as long as she consumes an equivalent amount of caffeine.Suppose that coffee has twice as much caffeine as tea.Which graph would illustrate a representative indifference curve?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If goods A and B are perfect substitutes,then the marginal rate of substitution of good A for good B is constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following diagram shows one indifference curve representing the preferences for goods X and Y for one consumer. 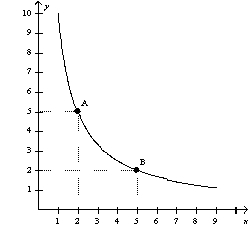 What is the marginal rate of substitution between points A and B?
What is the marginal rate of substitution between points A and B?
A) 2/5
B) 1
C) 5/2
D) 3
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The substitution effect in the work-leisure model induces a person to work less in response to higher wages,which tends to make the labor-supply curve slope upward.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Utility measures the
A) income a consumer receives from consuming a bundle of goods.
B) satisfaction a consumer receives from consuming a bundle of goods.
C) satisfaction a consumer places on her budget constraint.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Giffen good is a good for which
A) an increase in the price raises the quantity demanded.
B) the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C) an increase in the price decreases the quantity demanded.
D) Both a) and b) are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The theory of consumer choice provides a more complete understanding of supply,just as the theory of the competitive firm provides a more complete understanding of demand.
B) The theory of consumer choice provides a more complete understanding of demand,just as the theory of the competitive firm provides a more complete understanding of supply.
C) Monetary theory provides a more complete understanding of demand,just as the theory of the competitive firm provides a more complete understanding of supply.
D) The theory of public choice provides a more complete understanding of supply,just as the theory of the competitive firm provides a more complete understanding of demand.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The substitution effect from an increase in wages is evident in a
A) decrease in labor demand.
B) desire to consume less leisure.
C) desire to consume more leisure.
D) backward-bending labor supply curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pete consumes two goods,rice and fish.When the price of fish rises,he consumes less fish.When the price of rice rises,he consumes more rice.For Pete,
A) fish is not a Giffen good but rice is.
B) rice is not a Giffen good but fish is.
C) both fish and rice are normal goods.
D) both fish and rice are Giffen goods.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When economists describe preferences,they often use the concept of
A) markets.
B) income.
C) utility.
D) prices.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-11 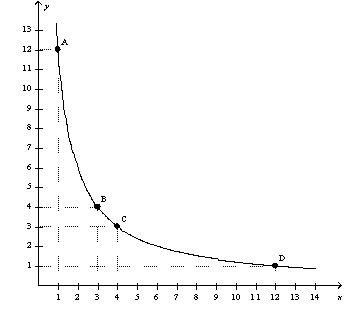 -Refer to Figure 21-11.The graph illustrates
-Refer to Figure 21-11.The graph illustrates
A) a typical budget constraint.
B) a typical indifference curve.
C) an indifference curve where goods X and Y are perfect complements.
D) an indifference curve where goods X and Y are perfect substitutes.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good is an inferior good if the consumer buys less of it when
A) his income rises.
B) the price of the good rises.
C) the price of a substitute good falls.
D) his income falls.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Giffen goods violate the law of demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-10 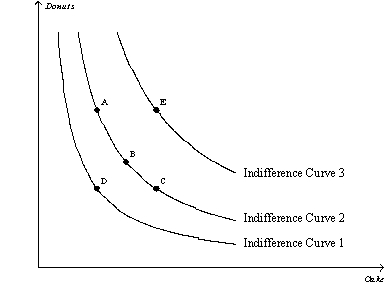 -Refer to Figure 21-10.Which of the following statements is correct?
-Refer to Figure 21-10.Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Bundle A provides the same utility as bundle E.
B) Bundle A provides the same utility as bundle C.
C) Bundle B contains more cake than bundle C.
D) The bundles along indifference curve Indifference Curve 2 are preferred to those along indifference curve Indifference Curve 3.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two goods are perfect substitutes,the marginal rate of substitution
A) is constant along the indifference curve.
B) decreases as the scarcity of one good increases.
C) increases as the scarcity of one good increases.
D) changes to reflect the consumer's changing preferences for the goods.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams