A) complex I
B) complex II
C) complex III
D) complex IV
E) All of the complexes can transfer electrons to O2.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron loses potential energy when it
A) shifts to a less electronegative atom.
B) shifts to a more electronegative atom.
C) increases its kinetic energy.
D) increases its activity as an oxidizing agent.
E) moves further away from the nucleus of the atom.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ATP made during fermentation is generated by which of the following?
A) the electron transport chain
B) substrate-level phosphorylation
C) chemiosmosis
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) aerobic respiration
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
A) glycolysis
B) accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
C) the citric acid cycle
D) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
E) the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis?
A) CO2 and H2O
B) CO2 and pyruvate
C) NADH and pyruvate
D) CO2 and NADH
E) H2O, FADH2, and citrate
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a friend who lost 7 kg (about 15 pounds) of fat on a regimen of strict diet and exercise. How did the fat leave her body?
A) It was released as CO2 and H2O.
B) It was converted to heat and then released.
C) It was converted to ATP, which weighs much less than fat.
D) It was broken down to amino acids and eliminated from the body.
E) It was converted to urine and eliminated from the body.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most accurately describes what is happening along the electron transport chain in Figure 7.2?
A) Chemiosmosis is coupled with electron transfer.
B) Each electron carrier alternates between being reduced and being oxidized.
C) ATP is generated at each step.
D) Energy of the electrons increases at each step.
E) Molecules in the chain give up some of their potential energy.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is proton-motive force?
A) the force required to remove an electron from hydrogen
B) the force provided by a transmembrane hydrogen ion gradient
C) the force that moves hydrogen into the intermembrane space
D) the force that moves hydrogen into the mitochondrion
E) the force that moves hydrogen to NAD+
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a molecule of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a proton) , the molecule becomes
A) dehydrogenated.
B) oxidized.
C) reduced.
D) redoxed.
E) hydrolyzed.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During glycolysis, when each molecule of glucose is catabolized to two molecules of pyruvate, most of the potential energy contained in glucose is
A) transferred to ADP, forming ATP.
B) transferred directly to ATP.
C) retained in the two pyruvates.
D) stored in the NADH produced.
E) used to phosphorylate fructose to form fructose 6-phosphate.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the molecule becomes
A) hydrolyzed.
B) hydrogenated.
C) oxidized.
D) reduced.
E) an oxidizing agent.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO2 and water is -686 kcal/mol and the free energy for the reduction of NAD+ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed?
A) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
B) Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
C) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
D) There is no CO2 or water produced as products of glycolysis.
E) Glycolysis consists of many enzymatic reactions, each of which extracts some energy from the glucose molecule.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis?
A) an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell
B) an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it
C) an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
D) an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+
E) an agent that blocks the passage of electrons along the electron transport chain
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What fraction of the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals is generated by the reactions of the citric acid cycle, if glucose is the sole energy source?
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 1/2
D) 2/3
E) all of it
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
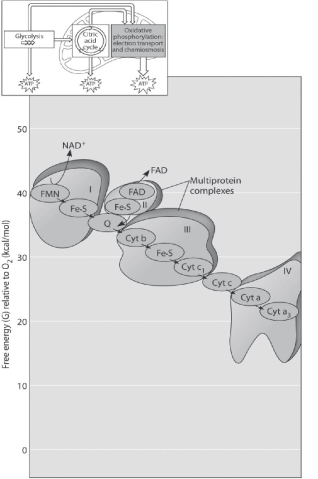 Figure 7.2
-Figure 7.2 shows the electron transport chain. Which of the following is the combination of substances that is initially added to the chain?
Figure 7.2
-Figure 7.2 shows the electron transport chain. Which of the following is the combination of substances that is initially added to the chain?
A) oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water
B) NAD+, FAD, and electrons
C) NADH, FADH2, and protons
D) NADH, FADH2, and O2
E) oxygen and protons
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where does glycolysis take place in eukaryotic cells?
A) mitochondrial matrix
B) mitochondrial outer membrane
C) mitochondrial inner membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) cytosol
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During aerobic respiration, H2O is formed. Where does the oxygen atom for the formation of the water come from?
A) carbon dioxide (CO2)
B) glucose (C6H12O6)
C) molecular oxygen (O2)
D) pyruvate (C3H3O3-)
E) lactate (C3H5O3-)
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what will happen to the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid in the citric acid cycle shown in Figure 7.1?
A) There will be no change in the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid.
B) Oxaloacetate will decrease and citric acid will accumulate.
C) Oxaloacetate will accumulate and citric acid will decrease.
D) Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will decrease.
E) Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will accumulate.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yeast cells that have defective mitochondria incapable of respiration will be able to grow by catabolizing which of the following carbon sources for energy?
A) glucose
B) proteins
C) fatty acids
D) glucose, proteins, and fatty acids
E) Such yeast cells will not be capable of catabolizing any food molecules, and will therefore die.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is formed by the removal of a carbon (as CO2) from a molecule of pyruvate?
A) lactate
B) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
C) oxaloacetate
D) acetyl CoA
E) citrate
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 90
Related Exams